C++ Exercises: Accept an integer (n) from the user and outputs the number of combinations that express n as a sum of two prime numbers
Goldbach Conjecture for n
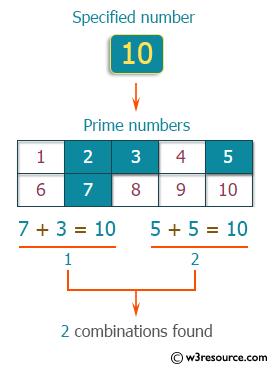
An even number of 4 or more can be represented by the sum of two prime numbers. This is called the Goldbach expectation, and it is confirmed that it is correct up to a considerable number by computer calculation. For example, 10 can be expressed as the sum of two prime numbers 7 + 3, 5 + 5. Write a C++ program that accepts an integer (n) from the user and outputs the number of combinations that express n as the sum of two prime numbers.
Note: n should be greater than or equal to 4 and less than or equal to 50,000.
Visual Presentation:
Sample Solution:
C++ Code :
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
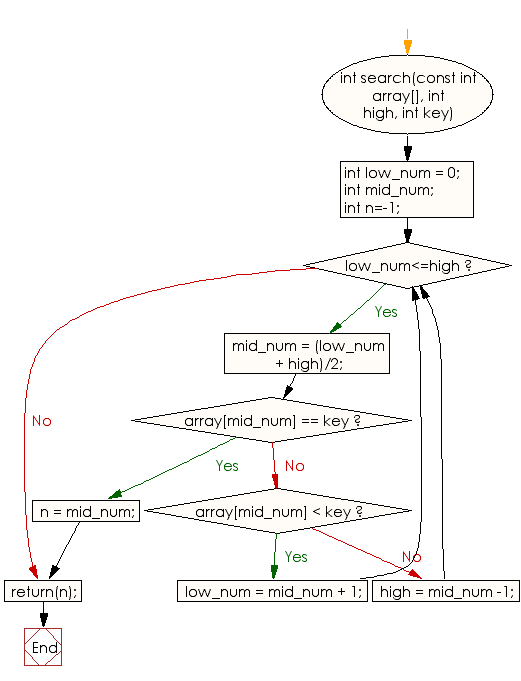
// Function to perform binary search in the array
int search(const int array[], int high, int key) {
int low_num = 0; // Initialize the lowest index to 0
int mid_num;
int n = -1; // Initialize 'n' to -1 (not found)
while (low_num <= high) { // Perform binary search until the lowest index is less than or equal to the highest index
mid_num = (low_num + high) / 2; // Calculate the middle index
if (array[mid_num] == key) { // If the key is found at the middle index
n = mid_num; // Set 'n' to the index where the key is found
break;
} else if (array[mid_num] < key) { // If the key is greater than the element at the middle index
low_num = mid_num + 1; // Update the lowest index to search the right subarray
} else { // If the key is smaller than the element at the middle index
high = mid_num - 1; // Update the highest index to search the left subarray
}
}
return (n); // Return the index where the key is found or -1 if not found
}
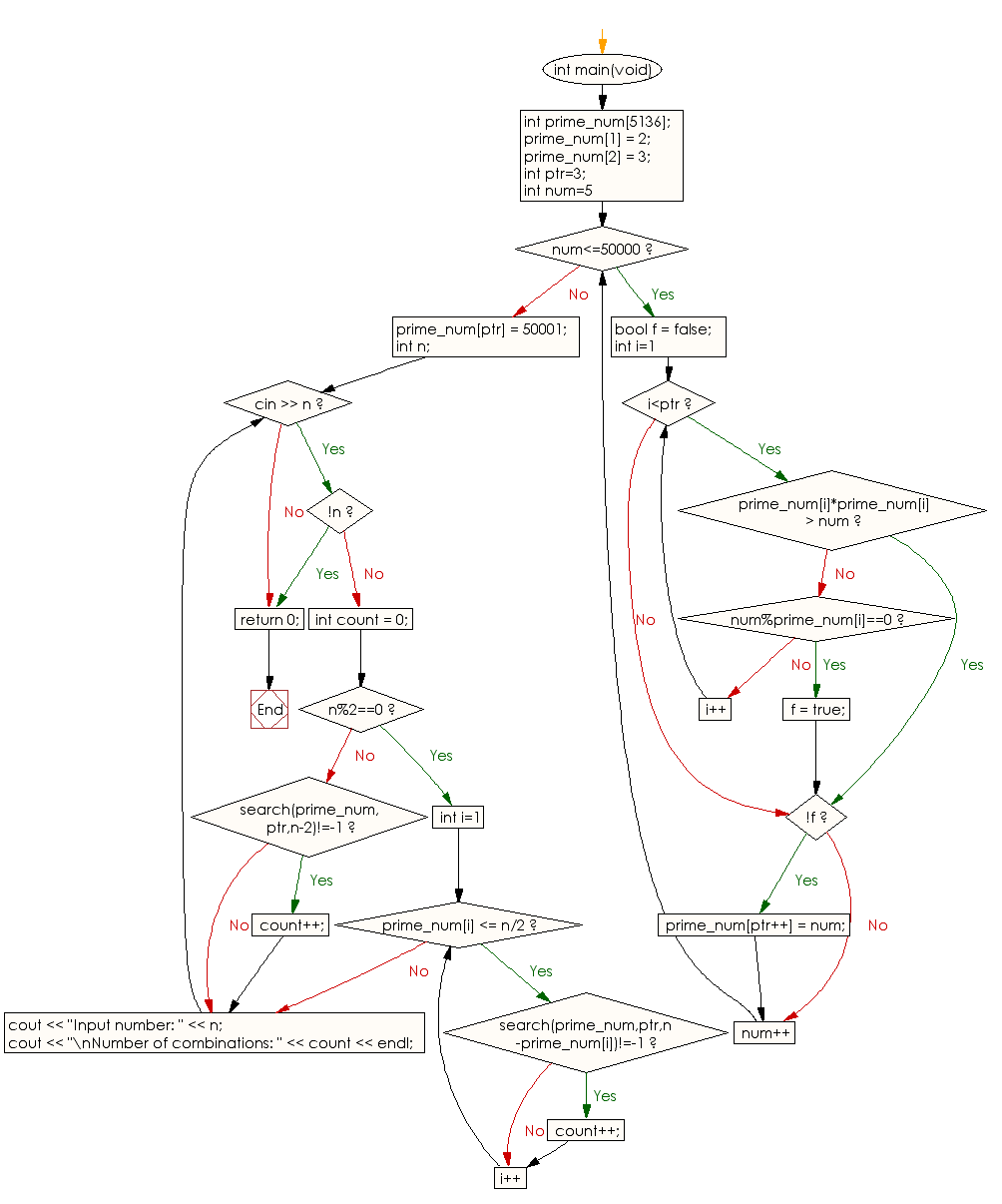
int main(void) {
int prime_num[5136]; // Array to store prime numbers
prime_num[1] = 2; // Set the first prime number
prime_num[2] = 3; // Set the second prime number
int ptr = 3; // Pointer to track the number of primes stored in the array
// Loop to find prime numbers and store them in the array
for (int num = 5; num <= 50000; num++) {
bool f = false; // Flag to check for divisibility
for (int i = 1; i < ptr; i++) {
if (prime_num[i] * prime_num[i] > num) { // If the square of prime number exceeds 'num', break the loop
break;
}
if (num % prime_num[i] == 0) { // If 'num' is divisible by any prime number, set flag and break loop
f = true;
break;
}
}
if (!f) { // If 'num' is not divisible by any prime number, store it in the array
prime_num[ptr++] = num;
}
}
prime_num[ptr] = 50001; // Set the last element of the array to a sentinel value
int n;
while (cin >> n) { // Input 'n' until EOF
if (!n) break; // Break the loop if 'n' is 0
int count = 0; // Counter to count combinations
if (n % 2 == 0) { // If 'n' is even
// Loop through prime numbers to find pairs that sum up to 'n'
for (int i = 1; prime_num[i] <= n / 2; i++) {
if (search(prime_num, ptr, n - prime_num[i]) != -1) // If complement of prime is found in the array
count++; // Increment count for valid pair
}
} else { // If 'n' is odd
if (search(prime_num, ptr, n - 2) != -1) // If 'n-2' is found in the array
count++; // Increment count for valid pair
}
// Output the input number and the count of combinations
cout << "Input number: " << n;
cout << "\nNumber of combinations: " << count << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Input number: 7 Number of combinations: 1 Input number: 85 Number of combinations: 1 Input number: 900 Number of combinations: 48 Input number: 1505 Number of combinations: 0
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program to find all pairs of prime numbers that sum up to an even number n using the Goldbach conjecture.
- Write a C++ program that accepts an even number n and outputs the count of distinct prime pairs whose sum equals n.
- Write a C++ program to verify Goldbach’s conjecture for numbers up to 50,000 by counting valid prime pairs for a given even n.
- Write a C++ program that reads an even number n, then outputs each pair of prime numbers that add up to n, and finally prints the total count.
Go to:
PREV : Sum of First n Primes.
NEXT : Orthogonal Lines Check.
C++ Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
