C Program: Binary Tree mirroring for a mirror image
6. Mirror Image Transformation Challenges
Write a C program to create a mirror image of a binary tree. Print both the original and mirrored trees.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
// Including necessary header files
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
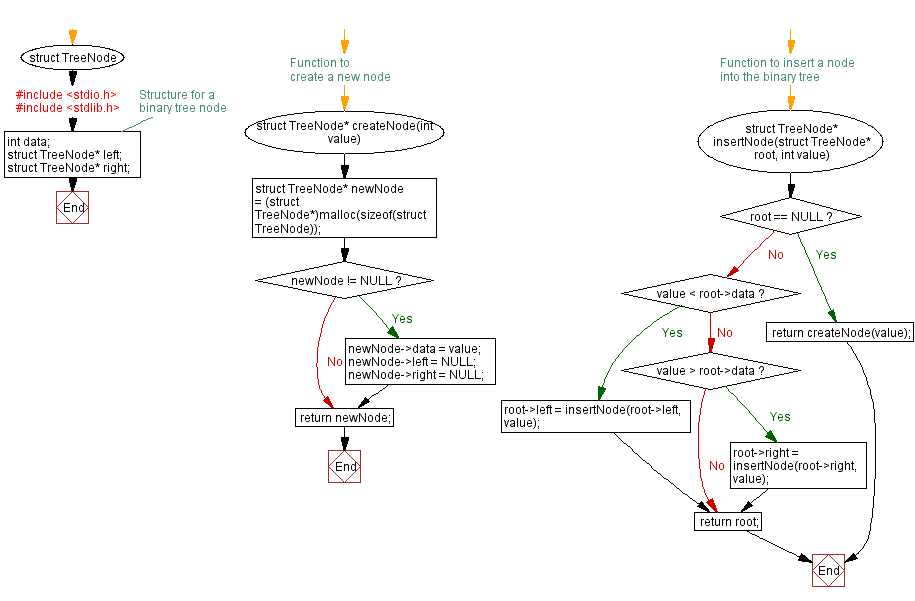
// Structure for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {
int data;
struct TreeNode* left;
struct TreeNode* right;
};
// Function to create a new node
struct TreeNode* createNode(int value) {
struct TreeNode* newNode = (struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
if (newNode != NULL) {
newNode->data = value;
newNode->left = NULL;
newNode->right = NULL;
}
return newNode;
}
// Function to insert a node into the binary tree
struct TreeNode* insertNode(struct TreeNode* root, int value) {
if (root == NULL) {
return createNode(value);
}
if (value < root->data) {
root->left = insertNode(root->left, value);
} else if (value > root->data) {
root->right = insertNode(root->right, value);
}
return root;
}
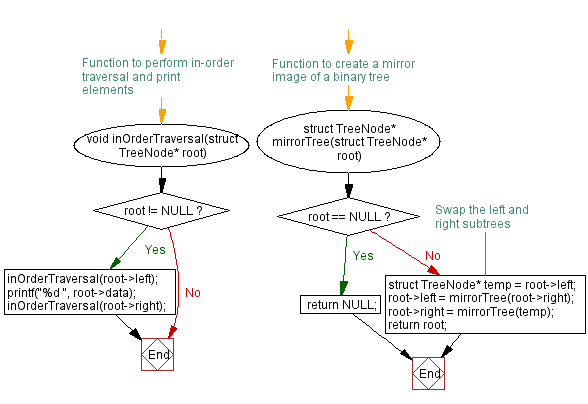
// Function to perform in-order traversal and print elements
void inOrderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root != NULL) {
inOrderTraversal(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
inOrderTraversal(root->right);
}
}
// Function to create a mirror image of a binary tree
struct TreeNode* mirrorTree(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
// Swap the left and right subtrees
struct TreeNode* temp = root->left;
root->left = mirrorTree(root->right);
root->right = mirrorTree(temp);
return root;
}
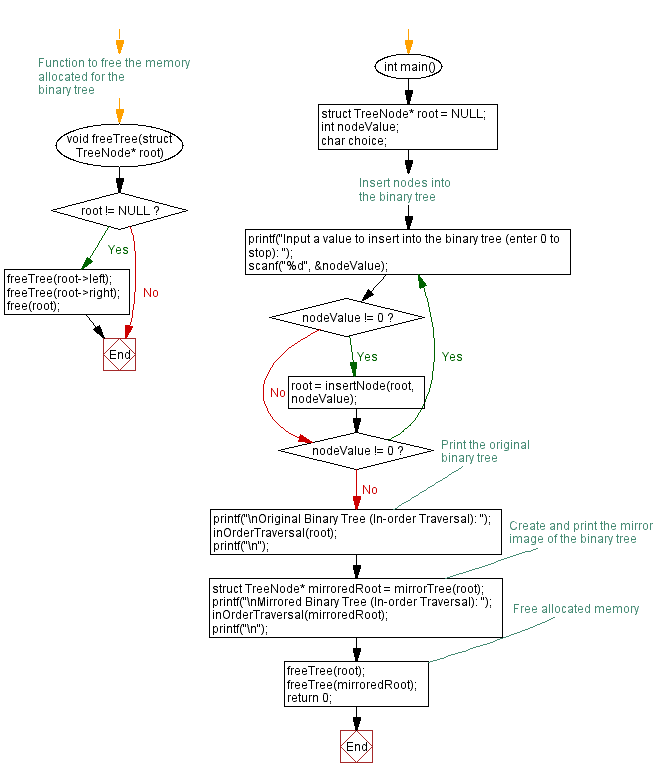
// Function to free the memory allocated for the binary tree
void freeTree(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root != NULL) {
freeTree(root->left);
freeTree(root->right);
free(root);
}
}
int main() {
struct TreeNode* root = NULL;
int nodeValue;
char choice;
// Insert nodes into the binary tree
do {
printf("Input a value to insert into the binary tree (enter 0 to stop): ");
scanf("%d", &nodeValue);
if (nodeValue != 0) {
root = insertNode(root, nodeValue);
}
} while (nodeValue != 0);
// Print the original binary tree
printf("\nOriginal Binary Tree (In-order Traversal): ");
inOrderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
// Create and print the mirror image of the binary tree
struct TreeNode* mirroredRoot = mirrorTree(root);
printf("\nMirrored Binary Tree (In-order Traversal): ");
inOrderTraversal(mirroredRoot);
printf("\n");
// Free allocated memory
freeTree(root);
freeTree(mirroredRoot);
return 0;
}
Output:
Input a value to insert into the binary tree (enter 0 to stop): 75 Input a value to insert into the binary tree (enter 0 to stop): 45 Input a value to insert into the binary tree (enter 0 to stop): 35 Input a value to insert into the binary tree (enter 0 to stop): 21 Input a value to insert into the binary tree (enter 0 to stop): 11 Input a value to insert into the binary tree (enter 0 to stop): 8 Input a value to insert into the binary tree (enter 0 to stop): 6 Input a value to insert into the binary tree (enter 0 to stop): 0 Original Binary Tree (In-order Traversal): 6 8 11 21 35 45 75 Mirrored Binary Tree (In-order Traversal): 75 45 35 21 11 8 6
Explanation:
In the exercise above,
- Node Structure (struct TreeNode):
- Represents a binary tree node with an integer data value, a pointer to the left child, and a pointer to the right child.
- createNode Function:
- Creates a new tree node with the given value and returns a pointer to it.
- insertNode Function:
- Inserts a new node into the binary tree while maintaining the binary search tree property.
- If the value is less than the current node's data, it goes to the left subtree; otherwise, it moves to the right subtree.
- inOrderTraversal Function:
- Performs in-order traversal of the binary tree, printing the elements in sorted order.
- mirrorTree Function:
- Creates a mirror image of the binary tree by swapping the left and right subtrees recursively.
- freeTree Function:
- Frees the memory allocated to the binary tree nodes recursively.
- main Function:
- Allows the user to input values to build the original binary tree.
- Prints the original tree using in-order traversal.
- Creates and prints the mirror image of the tree.
- Frees the allocated memory for both original and mirrored trees.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to create a mirror image of a binary tree and then verify if the in-order traversal of the mirror equals the reverse in-order of the original.
- Write a C program to generate the mirror image of a binary tree recursively and then mirror it back to the original form.
- Write a C program to mirror only the subtree rooted at a given node while leaving the rest of the tree unchanged.
- Write a C program to convert a binary tree into its mirror image and then print both trees side by side for comparison.
Go to:
PREV : Binary Tree Deletion Extensions.
NEXT : Level-Order Traversal Variants.
C Programming Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
