C Program: Binary search Tree insertion with sorted in-order traversal
3. Binary Search Tree Insertion Extensions
Write a C program that extends the binary tree program to support the insertion of elements. This is in a way that maintains the binary search tree property.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
// Including necessary header files
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure for a binary tree node
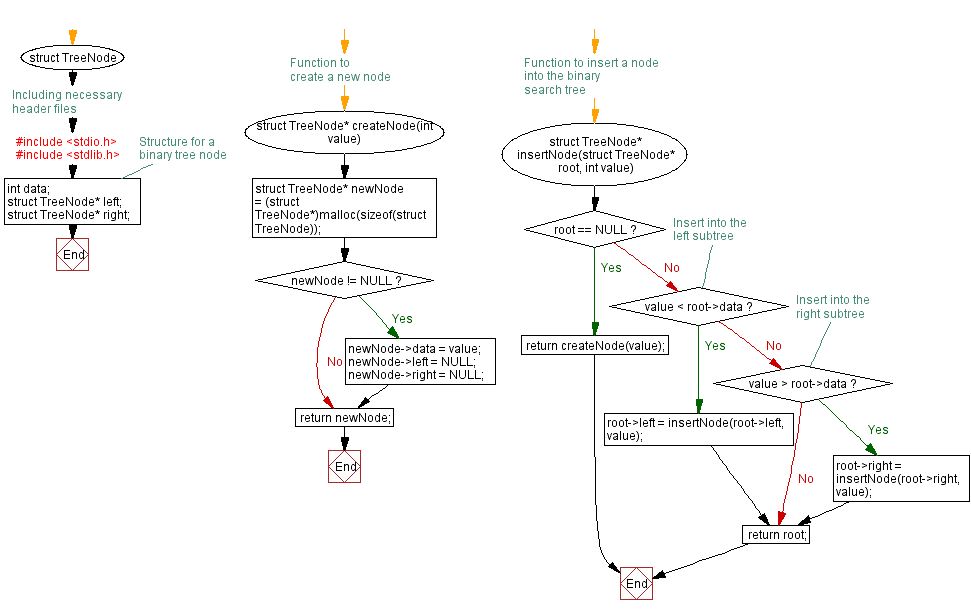
struct TreeNode {
int data;
struct TreeNode* left;
struct TreeNode* right;
};
// Function to create a new node
struct TreeNode* createNode(int value) {
struct TreeNode* newNode = (struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
if (newNode != NULL) {
newNode->data = value;
newNode->left = NULL;
newNode->right = NULL;
}
return newNode;
}
// Function to insert a node into the binary search tree
struct TreeNode* insertNode(struct TreeNode* root, int value) {
if (root == NULL) {
return createNode(value);
}
// Insert into the left subtree
if (value < root->data) {
root->left = insertNode(root->left, value);
}
// Insert into the right subtree
else if (value > root->data) {
root->right = insertNode(root->right, value);
}
return root;
}
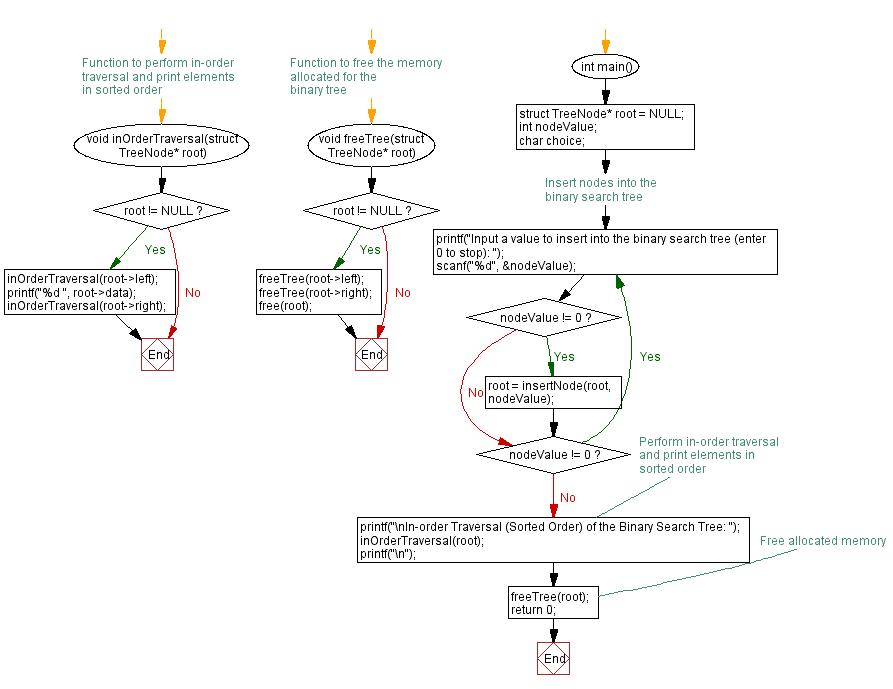
// Function to perform in-order traversal and print elements in sorted order
void inOrderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root != NULL) {
inOrderTraversal(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
inOrderTraversal(root->right);
}
}
// Function to free the memory allocated for the binary tree
void freeTree(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root != NULL) {
freeTree(root->left);
freeTree(root->right);
free(root);
}
}
int main() {
struct TreeNode* root = NULL;
int nodeValue;
char choice;
// Insert nodes into the binary search tree
do {
printf("Input a value to insert into the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): ");
scanf("%d", &nodeValue);
if (nodeValue != 0) {
root = insertNode(root, nodeValue);
}
} while (nodeValue != 0);
// Perform in-order traversal and print elements in sorted order
printf("\nIn-order Traversal (Sorted Order) of the Binary Search Tree: ");
inOrderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
// Free allocated memory
freeTree(root);
return 0;
}
Output:
Input a value to insert into the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): 72 Input a value to insert into the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): 51 Input a value to insert into the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): 42 Input a value to insert into the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): 12 Input a value to insert into the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): 10 Input a value to insert into the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): 0 In-order Traversal (Sorted Order) of the Binary Search Tree: 10 12 42 51 72
Explanation:
In the exercise above,
The above C program creates a binary search tree (BST) and allows users to insert elements into it while maintaining the BST property. Here's a brief explanation.
- Data Structure:
- The program defines a structure TreeNode to represent a node in the binary search tree. Each node contains an integer data, and pointers to the left and right children (left and right).
- Node Creation:
- The createNode function dynamically allocates memory for a new node and initializes its data and pointers. It returns a pointer to the newly created node.
- Insertion:
- The insertNode function inserts a new node into the binary search tree while maintaining the BST property.
- If the value is less than the current node's data, it is inserted into the left subtree. If greater, it goes into the right subtree.
- In-order Traversal:
- The inOrderTraversal function performs an in-order traversal of the binary search tree, printing the elements in sorted order.
- Memory Management:
- The freeTree function frees the memory allocated for the binary search tree by recursively freeing each node.
- Main Function:
- In the main function, the program allows users to input values to be inserted into the binary search tree. The insertion continues until the user enters 0.
- After insertion, the program performs an in-order traversal, displaying the elements in sorted order.
- Finally, it frees the memory allocated for the binary search tree.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to insert elements into a BST iteratively and verify the tree structure after each insertion.
- Write a C program to modify BST insertion to handle duplicate values by storing duplicates in a linked list at each node.
- Write a C program to insert nodes into a BST in random order and then perform a self-check to validate the BST property.
- Write a C program to implement a self-adjusting BST that performs splay operations after every insertion.
Go to:
PREV : In-Order Traversal Variants.
NEXT : Binary Tree Height Calculation Challenges.
C Programming Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
