C Program: Queue implementation using structure
7. Queue Implementation with Structures
Write a C program that implements a simple queue using a structure. The structure should contain an array representing the queue and front and rear indices. Include functions for enqueue and dequeue operations.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
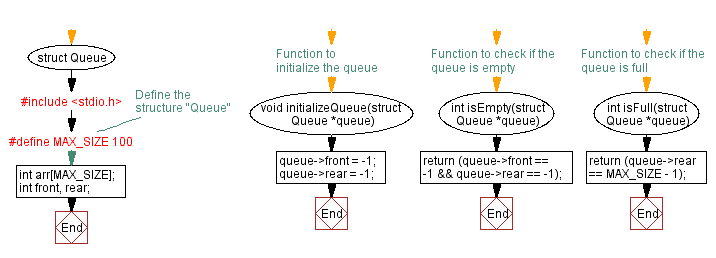
#include <stdio.h>
// Define the structure "Queue"
#define MAX_SIZE 100
struct Queue {
int arr[MAX_SIZE];
int front, rear;
};
// Function to initialize the queue
void initializeQueue(struct Queue *queue) {
queue->front = -1;
queue->rear = -1;
}
// Function to check if the queue is empty
int isEmpty(struct Queue *queue) {
return (queue->front == -1 && queue->rear == -1);
}
// Function to check if the queue is full
int isFull(struct Queue *queue) {
return (queue->rear == MAX_SIZE - 1);
}
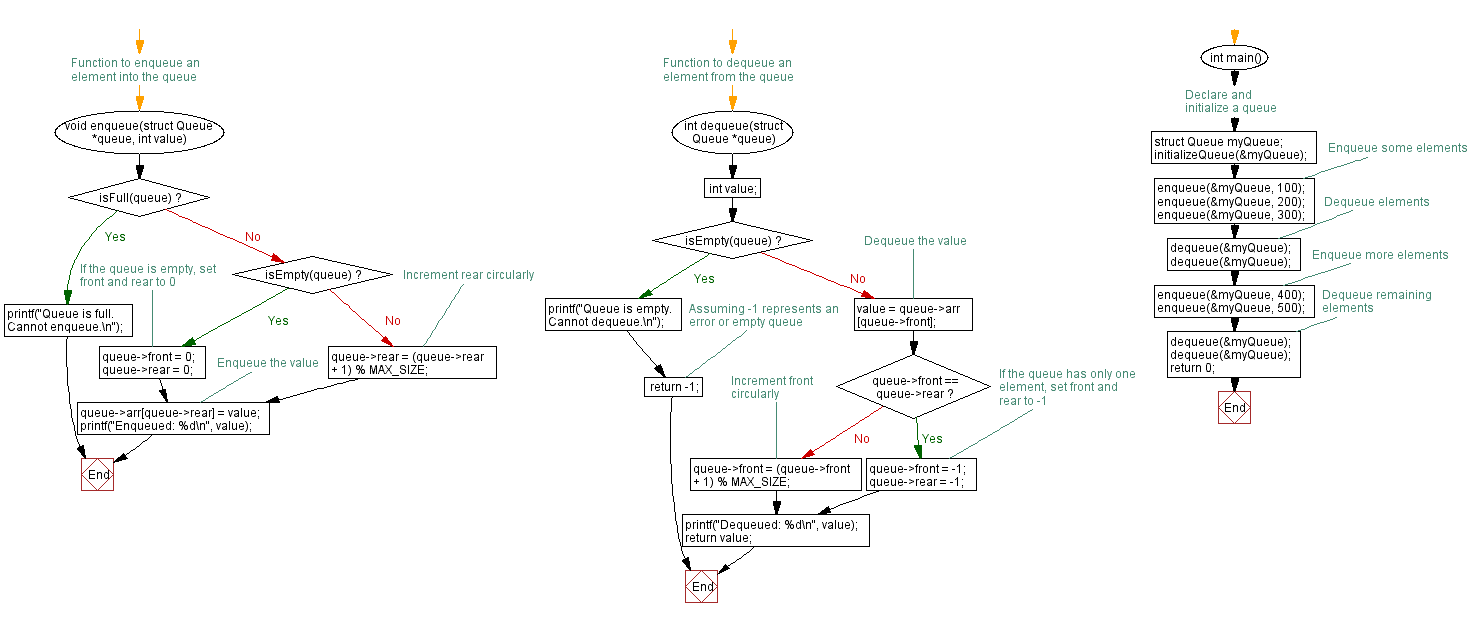
// Function to enqueue an element into the queue
void enqueue(struct Queue *queue, int value) {
if (isFull(queue)) {
printf("Queue is full. Cannot enqueue.\n");
return;
}
if (isEmpty(queue)) {
// If the queue is empty, set front and rear to 0
queue->front = 0;
queue->rear = 0;
} else {
// Increment rear circularly
queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
}
// Enqueue the value
queue->arr[queue->rear] = value;
printf("Enqueued: %d\n", value);
}
// Function to dequeue an element from the queue
int dequeue(struct Queue *queue) {
int value;
if (isEmpty(queue)) {
printf("Queue is empty. Cannot dequeue.\n");
return -1; // Assuming -1 represents an error or empty queue
}
// Dequeue the value
value = queue->arr[queue->front];
if (queue->front == queue->rear) {
// If the queue has only one element, set front and rear to -1
queue->front = -1;
queue->rear = -1;
} else {
// Increment front circularly
queue->front = (queue->front + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
}
printf("Dequeued: %d\n", value);
return value;
}
int main() {
// Declare and initialize a queue
struct Queue myQueue;
initializeQueue(&myQueue);
// Enqueue some elements
enqueue(&myQueue, 100);
enqueue(&myQueue, 200);
enqueue(&myQueue, 300);
// Dequeue elements
dequeue(&myQueue);
dequeue(&myQueue);
// Enqueue more elements
enqueue(&myQueue, 400);
enqueue(&myQueue, 500);
// Dequeue remaining elements
dequeue(&myQueue);
dequeue(&myQueue);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enqueued: 100 Enqueued: 200 Enqueued: 300 Dequeued: 100 Dequeued: 200 Enqueued: 400 Enqueued: 500 Dequeued: 300 Dequeued: 400
Explanation:
In the exercise above:
- The "Queue" structure is defined with an array '(arr)', 'front', and 'rear' indices.
- Functions like "initializeQueue()", "isEmpty()", and "isFull()" are used for queue management.
- The "enqueue()" function adds an element to the rear of the queue.
- The "dequeue()" function removes an element from the front of the queue.
- The "main()" function demonstrates the usage of the queue operations.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to implement a simple queue using a structure, including functions for enqueue, dequeue, and display operations.
- Write a C program to implement a circular queue using a structure and handle overflow and underflow conditions.
- Write a C program to implement a queue using a structure, then reverse the order of the elements in the queue.
- Write a C program to implement a priority queue using a structure where each element has an associated priority, and perform insertion and deletion based on priority.
Go to:
PREV : Date Structure Operations.
NEXT : Complex Number Operations.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
