C Exercises: Implement a stack using a singly linked list
2. Linked List Stack Variants
Write a C program to implement a stack using a singly linked list.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Node structure to represent elements in the stack
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// Stack structure to manage the stack
struct Stack {
struct Node* top;
};
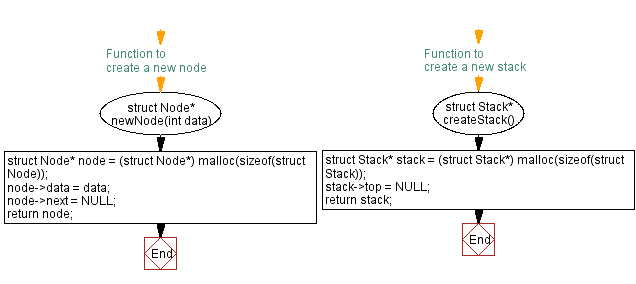
// Function to create a new node with given data
struct Node* newNode(int data) {
struct Node* node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = data;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
// Function to create a new stack and initialize it
struct Stack* createStack() {
struct Stack* stack = (struct Stack*) malloc(sizeof(struct Stack));
stack->top = NULL;
return stack;
}
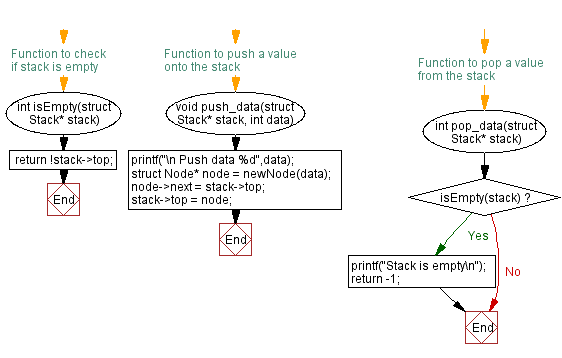
// Function to check if the stack is empty
int isEmpty(struct Stack* stack) {
return !stack->top; // Returns 1 if the stack is empty, otherwise returns 0
}
// Function to push a value onto the stack
void push_data(struct Stack* stack, int data) {
printf("\n Push data %d", data);
struct Node* node = newNode(data);
node->next = stack->top;
stack->top = node; // The new node becomes the top of the stack
}
// Function to pop a value from the stack
int pop_data(struct Stack* stack) {
if (isEmpty(stack)) {
printf("Stack is empty\n");
return -1; // Returns -1 if the stack is empty
}
struct Node* temp = stack->top;
int popped = temp->data; // Value to be popped from the top of the stack
stack->top = temp->next; // Move the top pointer to the next node
free(temp); // Free the memory of the popped node
return popped; // Return the popped value
}
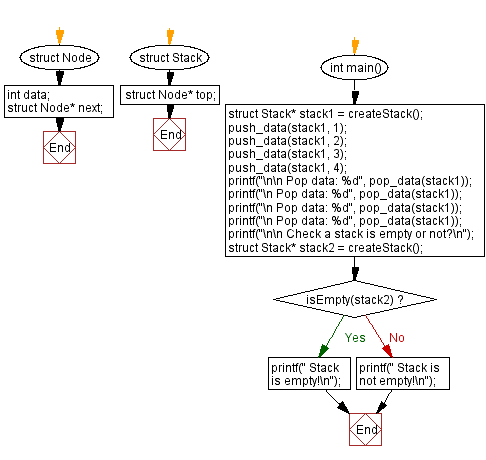
int main() {
// Creating a stack and pushing elements onto it
struct Stack* stack1 = createStack();
push_data(stack1, 1);
push_data(stack1, 2);
push_data(stack1, 3);
push_data(stack1, 4);
// Popping elements from the stack and displaying them
printf("\n\n Pop data: %d", pop_data(stack1));
printf("\n Pop data: %d", pop_data(stack1));
printf("\n Pop data: %d", pop_data(stack1));
printf("\n Pop data: %d", pop_data(stack1));
// Checking if a stack is empty or not
printf("\n\n Check a stack is empty or not?\n");
struct Stack* stack2 = createStack();
if (isEmpty(stack2)) {
printf(" Stack is empty!\n");
} else {
printf(" Stack is not empty!\n");
}
}
Output:
Push data 1 Push data 2 Push data 3 Push data 4 Pop data: 4 Pop data: 3 Pop data: 2 Pop data: 1 Check a stack is empty or not? Stack is empty!
Flowchart
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to implement a stack using a singly linked list that supports retrieving the minimum element in O(1) time.
- Write a C program to reverse a stack implemented via a singly linked list using recursion without extra memory.
- Write a C program to remove duplicate elements from a stack implemented with a singly linked list.
- Write a C program to merge two stacks (each implemented as a singly linked list) into one sorted stack.
Go to:
PREV : Array Stack Extended Challenges.
NEXT : Array Stack Capacity Checks.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.