C Exercises: Sort numbers using Binary insertion Sort method
26. Binary Insertion Sort Variants
Write a C program that sorts numbers using the Binary insertion sort method.
Binary insertion sort employs a binary search to determine the correct location to insert new elements, and therefore performs ⌈log2 n⌉ comparisons in the worst case, which is O(n log n).
Sample Solution:
Sample C Code:
# include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Function to perform binary search and find the index for insertion
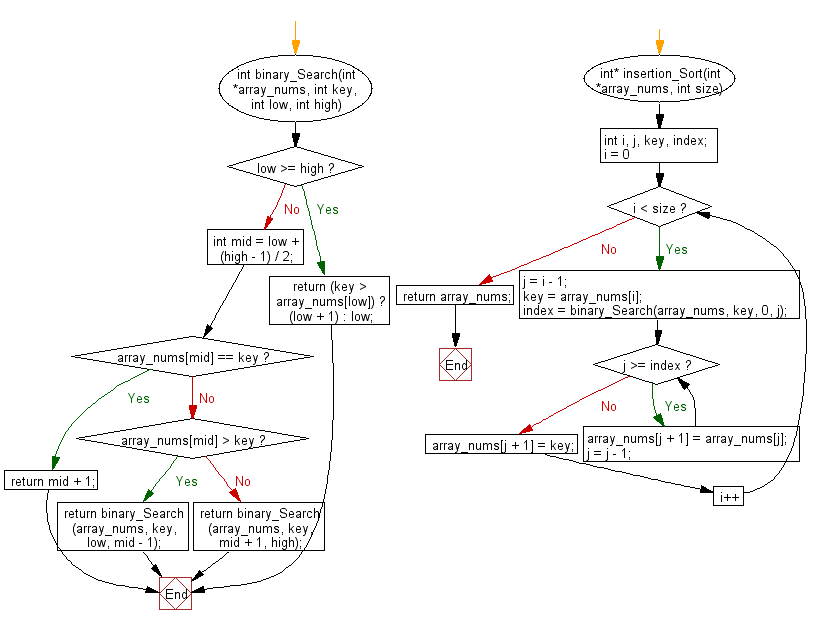
int binary_Search(int *array_nums, int key, int low, int high)
{
// Base case: when the search space is reduced to a single element
if (low >= high)
return (key > array_nums[low]) ? (low + 1) : low;
// Calculate the middle index
int mid = low + (high - 1) / 2;
// Check if the key is at the middle index
if (array_nums[mid] == key)
return mid + 1;
// If the key is smaller, search in the left subarray
else if (array_nums[mid] > key)
return binary_Search(array_nums, key, low, mid - 1);
// If the key is larger, search in the right subarray
else
return binary_Search(array_nums, key, mid + 1, high);
}
// Function to perform insertion sort on an array
int* insertion_Sort(int *array_nums, int size)
{
int i, j, key, index;
// Iterate through each element in the array
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
j = i - 1;
key = array_nums[i];
// Use binary search to find the index for inserting the key
index = binary_Search(array_nums, key, 0, j);
// Shift elements to make space for the key
while (j >= index)
{
array_nums[j + 1] = array_nums[j];
j = j - 1;
}
// Insert the key at the correct position
array_nums[j + 1] = key;
}
// Return the sorted array
return array_nums;
}
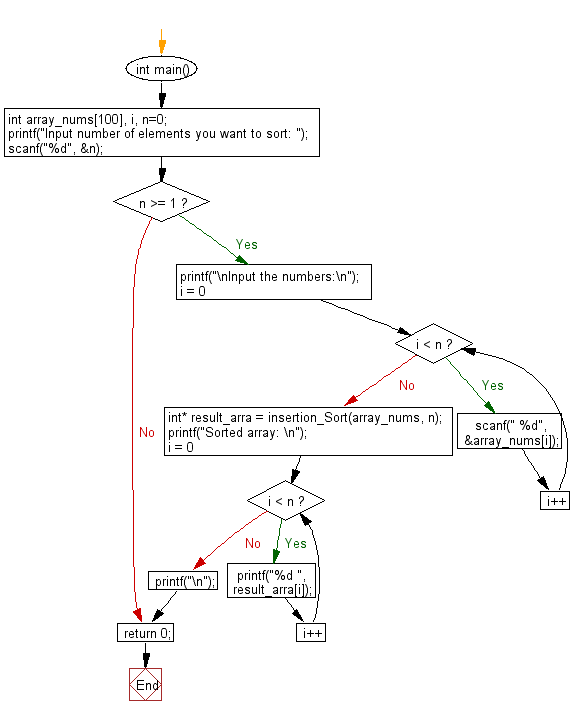
int main()
{
int array_nums[100], i, n=0;
printf("Input number of elements you want to sort: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
// Check if the input size is valid
if (n >= 1)
{
printf("\nInput the numbers:\n");
// Input the numbers into the array
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf(" %d", &array_nums[i]);
// Call the insertion_Sort function to sort the array
int* result_arra = insertion_Sort(array_nums, n);
// Display the sorted array
printf("Sorted array: \n");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%d ", result_arra[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Input number of elements you want to sort: 5 Input the numbers: 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 Sorted array: 5 10 15 20 25 -------------------------------- Process exited after 18.22 seconds with return value 0 Press any key to continue . . .
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to implement binary insertion sort on an array and count the number of binary comparisons made.
- Write a C program to sort an array of integers using binary insertion sort and then verify the sorted order by printing the array.
- Write a C program to modify binary insertion sort to sort an array in descending order using a custom comparator.
- Write a C program to implement binary insertion sort on an array of structures using a specific field as the key.
Go to:
PREV : Bucket Sort Variants.
NEXT : C Programming Challenges Exercises Home
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
