C Exercises: Sort numbers using Cycle Sort method
15. Cycle Sort Variants
Write a C program that sorts numbers using the Cycle sort method.
Cycle sort is an in-place, unstable sorting algorithm, a comparison sort that is theoretically optimal in terms of the total number of writes to the original array, unlike any other in-place sorting algorithm. It is based on the idea that the permutation to be sorted can be factored into cycles, which can individually be rotated to give a sorted result.
Sample Solution:
Sample C Code:
// CycleSort Implementation
// Source: https://bit.ly/2rcvXK5
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Function to perform CycleSort on an array in place
// and return the number of writes.
int cycleSort(int *list, size_t l_len);
// Function to display the elements of an array
void show_array(int *array, size_t a_len);
// Implementation of CycleSort algorithm
int cycleSort(int *list, size_t l_len) {
int cycleStart, writes = 0;
// Loop through the array to find cycles to rotate
for (cycleStart = 0; cycleStart < l_len - 1; ++cycleStart) {
int item = list[cycleStart];
int swap_tmp, i;
// Find where to put the item
int pos = cycleStart;
for (i = cycleStart + 1; i < l_len; ++i) {
if (list[i] < item) {
++pos;
}
}
// If the item is already there, this is not a cycle
if (pos == cycleStart) {
continue;
}
// Otherwise, put the item there or right after any duplicates
while (item == list[pos]) {
++pos;
}
swap_tmp = list[pos];
list[pos] = item;
item = swap_tmp;
++writes;
// Rotate the rest of the cycle
while (pos != cycleStart) {
// Find where to put the item
pos = cycleStart;
for (i = cycleStart + 1; i < l_len; ++i) {
if (list[i] < item) {
++pos;
}
}
// Put the item there or right after any duplicates
while (item == list[pos]) {
++pos;
}
swap_tmp = list[pos];
list[pos] = item;
item = swap_tmp;
++writes;
}
}
return writes;
}
// Main function
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int arr[] = {0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 9, 3, 5, 5, 8, 4, 7, 0, 6};
int arr_k = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int writes, i;
// Display original array
printf("Original Array:\n");
show_array(arr, arr_k);
// Sort the array using CycleSort
writes = cycleSort(arr, arr_k);
// Display sorted array and number of writes
printf("\nSorted Array:\n");
show_array(arr, arr_k);
printf("writes: %d\n", writes);
return 0;
}
// Function to display the elements of an array
void show_array(int *array, size_t a_len) {
int ix;
for (ix = 0; ix < a_len; ++ix) {
printf("%d ", array[ix]);
}
putchar('\n');
return;
}
Sample Output:
Original Array: 0 1 2 2 2 2 1 9 3 5 5 8 4 7 0 6 Sorted Array: 0 0 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 4 5 5 6 7 8 9 writes: 10
Flowchart:
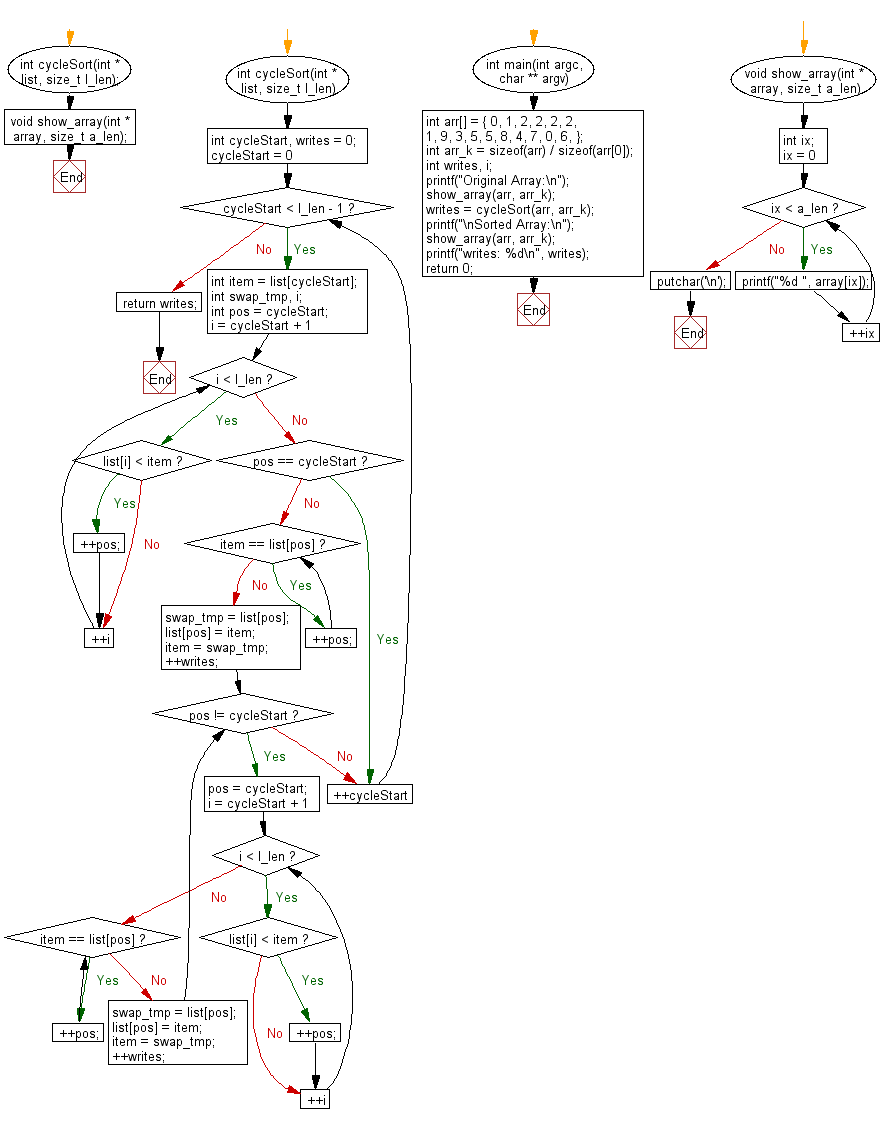
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to implement cycle sort on an array and output the total number of writes performed.
- Write a C program to modify cycle sort to sort an array in descending order.
- Write a C program to implement cycle sort on an array with duplicate values and verify its stability.
- Write a C program to compare cycle sort with selection sort by counting element movements.
Go to:
PREV : Cocktail Sort Variants.
NEXT : Permutation Sort Variants.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
