C Exercises: Pair in a linked list whose sum is equal to a given value
38. Pair Sum Search Challenges
Write a C program to find a pair in a singly linked list whose sum is equal to a given value.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
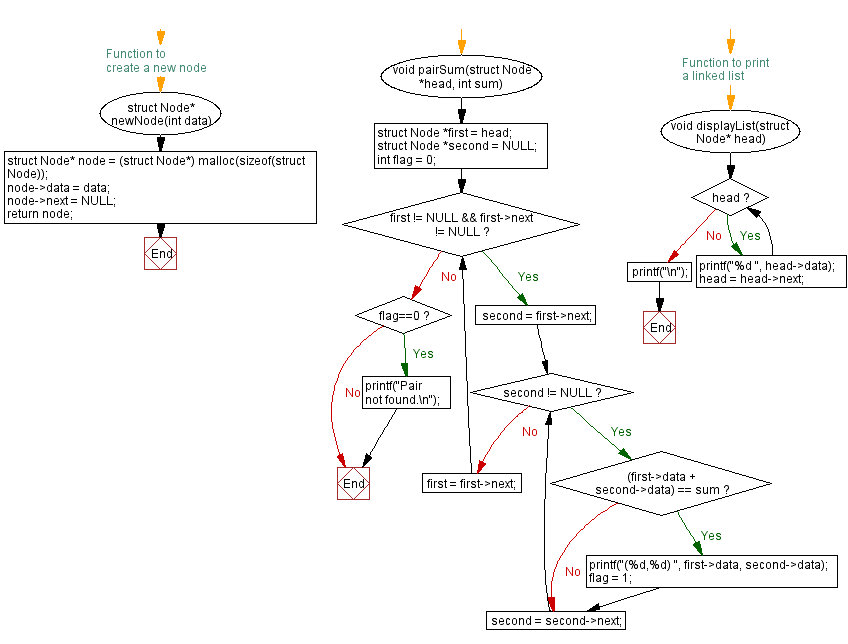
// Structure defining a node in a singly linked list
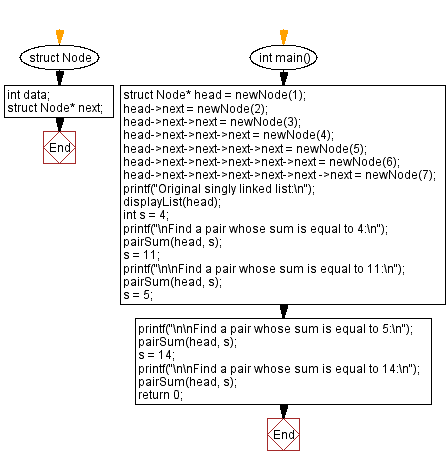
struct Node {
int data; // Data stored in the node
struct Node* next; // Pointer to the next node
};
// Function to create a new node with given data
struct Node* newNode(int data) {
struct Node* node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); // Allocate memory for a new node
node->data = data; // Assign data to the new node
node->next = NULL; // Initialize the next pointer as NULL
return node; // Return the newly created node
}
// Function to find pairs in a linked list that sum up to a given value
void pairSum(struct Node *head, int sum) {
struct Node *first = head; // Pointer for the first node
struct Node *second = NULL; // Pointer for the second node
int flag = 0; // Flag to indicate if pairs are found
// Loop through the list
while (first != NULL && first->next != NULL) {
second = first->next; // Initialize second pointer to the node after the first
// Loop to compare each node's data with other nodes' data in the list
while (second != NULL) {
if ((first->data + second->data) == sum) { // Check if the sum matches the given value
printf("(%d,%d) ", first->data, second->data); // Print the pair
flag = 1; // Set the flag to indicate pair(s) found
}
second = second->next; // Move the second pointer to the next node
}
first = first->next; // Move the first pointer to the next node
}
if(flag==0)
printf("Pair not found.\n"); // If no pairs found, print message
}
// Function to print elements of a linked list
void displayList(struct Node* head) {
while (head) {
printf("%d ", head->data); // Print the data of the current node
head = head->next; // Move to the next node
}
printf("\n");
}
// Main function to demonstrate finding pairs in a linked list that sum up to a given value
int main() {
struct Node* head = newNode(1); // Create the linked list with some initial nodes
head->next = newNode(2);
head->next->next = newNode(3);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(5);
head->next->next->next->next->next = newNode(6);
head->next->next->next->next->next ->next = newNode(7);
printf("Original singly linked list:\n");
displayList(head); // Display the original list
int s = 4; // The sum value to find pairs
printf("\nFind a pair whose sum is equal to 4:\n");
pairSum(head, s); // Find pairs that sum up to 4
// Test with different sum values
s = 11;
printf("\n\nFind a pair whose sum is equal to 11:\n");
pairSum(head, s);
s = 5;
printf("\n\nFind a pair whose sum is equal to 5:\n");
pairSum(head, s);
s = 14;
printf("\n\nFind a pair whose sum is equal to 14:\n");
pairSum(head, s);
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Original singly linked list: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Find a pair whose sum is equal to 4: (1,3) Find a pair whose sum is equal to 11: (4,7) (5,6) Find a pair whose sum is equal to 5: (1,4) (2,3) Find a pair whose sum is equal to 14: Pair not found.
Flowchart :
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to find all unique pairs in a singly linked list whose sum equals a given target without using extra space.
- Write a C program to find a pair whose product equals a given value in a singly linked list.
- Write a C program to sort a linked list and then use a two-pointer approach to find pairs that sum to a target value.
- Write a C program to identify and print multiple pairs from a linked list that add up to a given sum, handling duplicates appropriately.
Go to:
PREV : Delete all elements greater than x from a linked list.
Next: Alternate Interleaving Challenges.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
