C Exercises: Combine k sorted linked lists into a single sorted linked list
29. Merging K Sorted Lists Challenges
Write a C program to merge k sorted linked lists into a single sorted linked list.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure for defining a Node in a Singly Linked List
struct Node {
int data; // Data stored in the node
struct Node* next; // Pointer to the next node
};
// Function to create a new node in the Singly Linked List
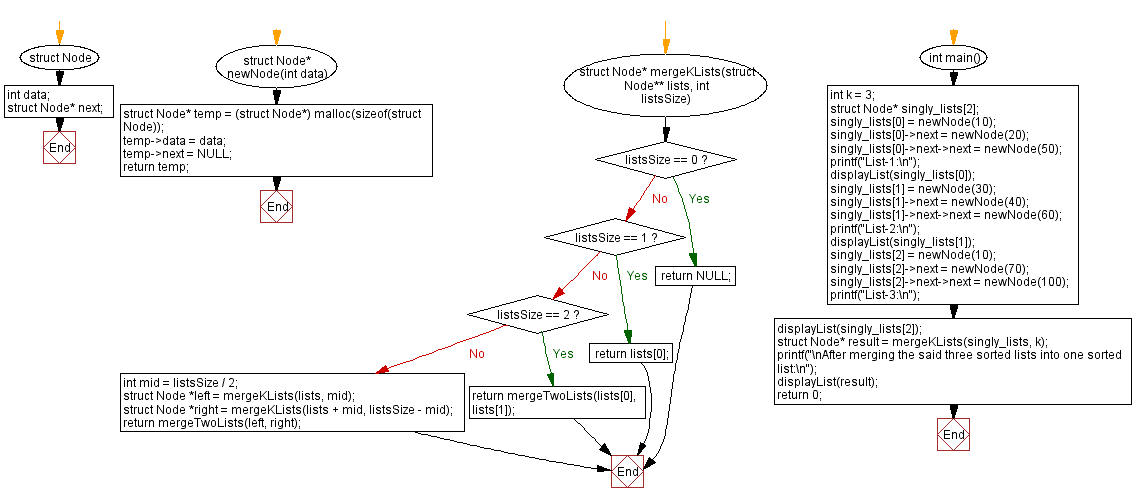
struct Node* newNode(int data) {
struct Node* temp = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); // Allocate memory for a new node
temp->data = data; // Assign the data to the new node
temp->next = NULL; // Initialize next pointer as NULL
return temp; // Return the new node
}
// Function to display a linked list
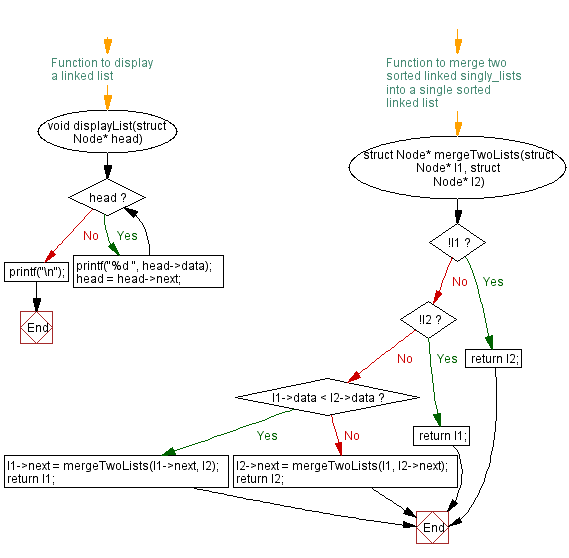
void displayList(struct Node* head) {
while (head) {
printf("%d ", head->data); // Print the data of the current node
head = head->next; // Move to the next node
}
printf("\n");
}
// Function to merge two sorted linked singly_lists into a single sorted linked list
struct Node* mergeTwoLists(struct Node* l1, struct Node* l2) {
if (!l1) return l2; // If l1 is empty, return l2
if (!l2) return l1; // If l2 is empty, return l1
if (l1->data < l2->data) {
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2); // Merge remaining lists after l1
return l1; // Return merged list with l1 as the starting node
} else {
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next); // Merge remaining lists after l2
return l2; // Return merged list with l2 as the starting node
}
}
// Function to merge k sorted lists into one sorted list
struct Node* mergeKLists(struct Node** lists, int listsSize) {
if (listsSize == 0) return NULL; // If there are no lists, return NULL
if (listsSize == 1) return lists[0]; // If only one list, return that list
if (listsSize == 2) return mergeTwoLists(lists[0], lists[1]); // If two lists, merge them
int mid = listsSize / 2;
struct Node *left = mergeKLists(lists, mid); // Merge the first half of lists
struct Node *right = mergeKLists(lists + mid, listsSize - mid); // Merge the second half of lists
return mergeTwoLists(left, right); // Merge the two merged halves
}
// Main function
int main() {
int k = 3; // Number of lists to be merged
struct Node* singly_lists[3]; // Array of pointers to linked lists
singly_lists[0] = newNode(10); // Create and populate List-1
singly_lists[0]->next = newNode(20);
singly_lists[0]->next->next = newNode(50);
printf("List-1:\n");
displayList(singly_lists[0]);
singly_lists[1] = newNode(30); // Create and populate List-2
singly_lists[1]->next = newNode(40);
singly_lists[1]->next->next = newNode(60);
printf("List-2:\n");
displayList(singly_lists[1]);
singly_lists[2] = newNode(10); // Create and populate List-3
singly_lists[2]->next = newNode(70);
singly_lists[2]->next->next = newNode(100);
printf("List-3:\n");
displayList(singly_lists[2]);
struct Node* result = mergeKLists(singly_lists, k); // Merge the k lists
printf("\nAfter merging the said three sorted lists into one sorted list:\n");
displayList(result); // Display the merged list
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
List-1: 10 20 50 List-2: 30 40 60 List-3: 10 70 100 After merging the said three sorted lists into one sorted list: 10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 100
Flowchart :
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to merge k sorted linked lists using a divide and conquer strategy.
- Write a C program to merge k sorted linked lists and simultaneously remove duplicate nodes during the merge.
- Write a C program to merge k sorted linked lists where each list is sorted in descending order, then output in ascending order.
- Write a C program to merge k sorted linked lists using a simulated min-heap approach in C.
Go to:
PREV : Nth Node Removal Variants.
NEXT : Reordering by Parity Challenges.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
