C Exercises: Rotate a singly linked list to the right by k places
23. List Rotation Challenges
Write a C program that rotates a singly linked list to the right by k places.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
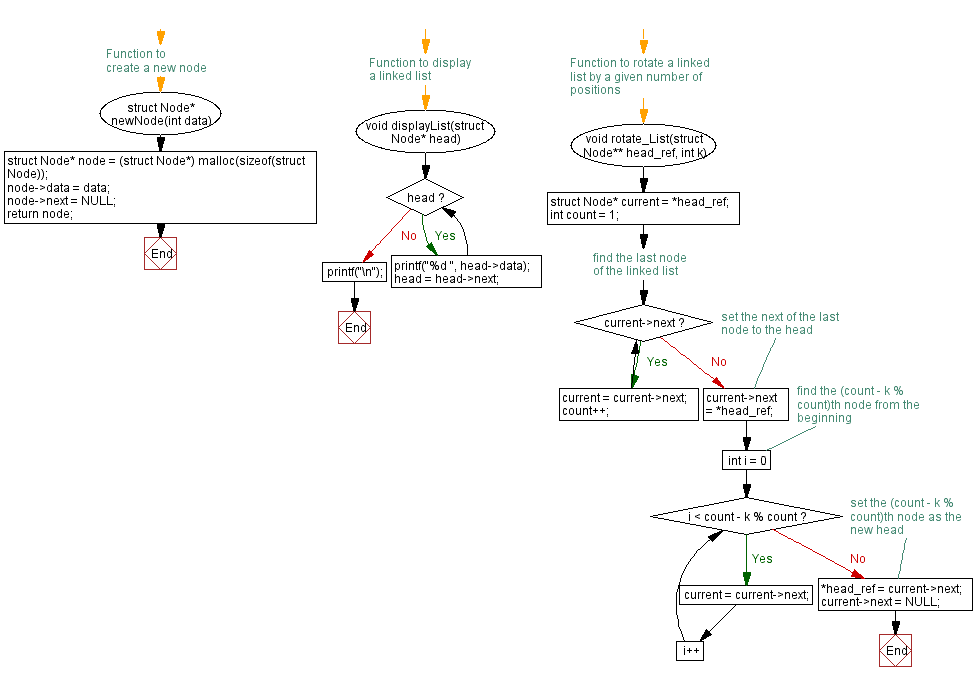
// Define a structure for a Node in a singly linked list
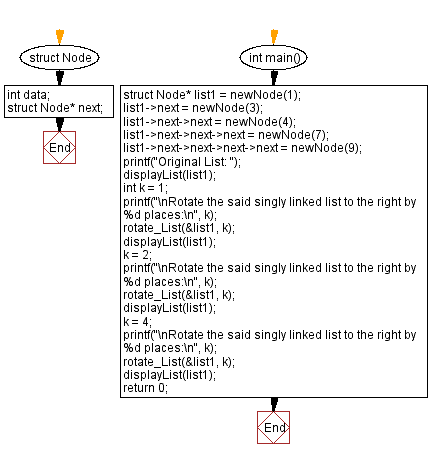
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// Function to create a new node with given data
struct Node* newNode(int data) {
// Allocate memory for a new node
struct Node* node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Set the data for the new node
node->data = data;
// Set the next pointer of the new node to NULL
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
// Function to display the elements of a linked list
void displayList(struct Node* head) {
while (head) {
printf("%d ", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// Function to rotate a linked list by a given number of positions
void rotate_List(struct Node** head_ref, int k) {
struct Node* current = *head_ref;
int count = 1;
// Find the last node of the linked list and count the total nodes
while (current->next) {
current = current->next;
count++;
}
// Set the next of the last node to the head, making it circular
current->next = *head_ref;
// Find the (count - k % count)th node from the beginning
for (int i = 0; i < count - k % count; i++) {
current = current->next;
}
// Set the (count - k % count)th node as the new head and break the link to form a new tail
*head_ref = current->next;
current->next = NULL;
}
// Main function where the execution starts
int main() {
// Creating a linked list
struct Node* list1 = newNode(1);
list1->next = newNode(3);
list1->next->next = newNode(4);
list1->next->next->next = newNode(7);
list1->next->next->next->next = newNode(9);
printf("Original List: ");
displayList(list1); // Display the original list
int k = 1;
printf("\nRotate the said singly linked list to the right by %d places:\n", k);
rotate_List(&list1, k); // Rotate the list by k places to the right
displayList(list1); // Display the rotated list
k = 2;
printf("\nRotate the said singly linked list to the right by %d places:\n", k);
rotate_List(&list1, k); // Rotate the list by k places to the right
displayList(list1); // Display the rotated list
k = 4;
printf("\nRotate the said singly linked list to the right by %d places:\n", k);
rotate_List(&list1, k); // Rotate the list by k places to the right
displayList(list1); // Display the rotated list
return 0; // Indicates successful completion of the program
}
Sample Output:
Original List: 1 3 4 7 9 Rotate the said singly linked list to the right by 1 places: 9 1 3 4 7 Rotate the said singly linked list to the right by 2 places: 4 7 9 1 3 Rotate the said singly linked list to the right by 4 places: 7 9 1 3 4
Flowchart :
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to rotate a singly linked list to the left by k places without computing the list's length.
- Write a C program to rotate a linked list by k places where k can be negative, indicating a left rotation.
- Write a C program to rotate a circular linked list by k places and then break the circle to restore a standard list.
- Write a C program to rotate a linked list using a recursive approach to shift nodes one by one.
PREV : Linked List Addition Variants.
NEXT :Kth Node Swapping Variants.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
