C Exercises: Copy of a singly linked list with random pointers
18. Copy with Random Pointers Challenges
Write a C program to create a copy of a singly linked list with random pointers.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
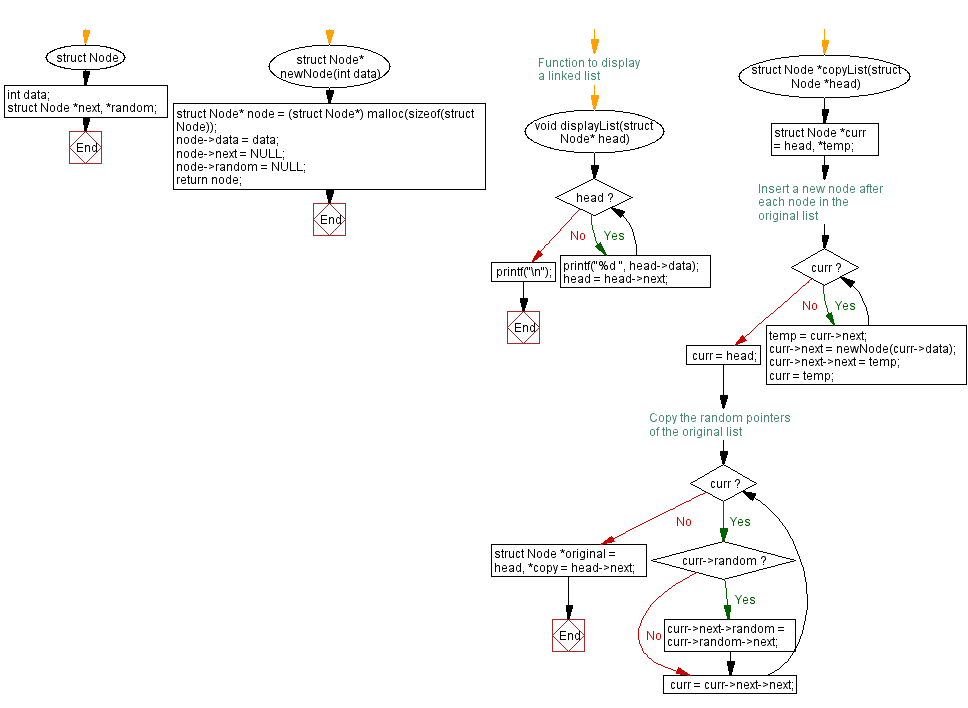
// Define a structure for a Node in a singly linked list
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *next, *random;
};
// Function to create a new node with given data
struct Node* newNode(int data) {
// Allocate memory for a new node
struct Node* node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Set the data for the new node
node->data = data;
// Set the next and random pointers of the new node to NULL
node->next = NULL;
node->random = NULL;
return node;
}
// Function to display the elements of a linked list
void displayList(struct Node* head) {
while (head) {
printf("%d ", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// Function to perform deep copy of a linked list with random pointers
struct Node *copyList(struct Node *head) {
struct Node *curr = head, *temp;
// Insert a new node after each node in the original list
while (curr) {
temp = curr->next;
curr->next = newNode(curr->data);
curr->next->next = temp;
curr = temp;
}
curr = head;
// Copy the random pointers of the original list
while (curr) {
if (curr->random)
curr->next->random = curr->random->next;
curr = curr->next->next;
}
struct Node *original = head, *copy = head->next;
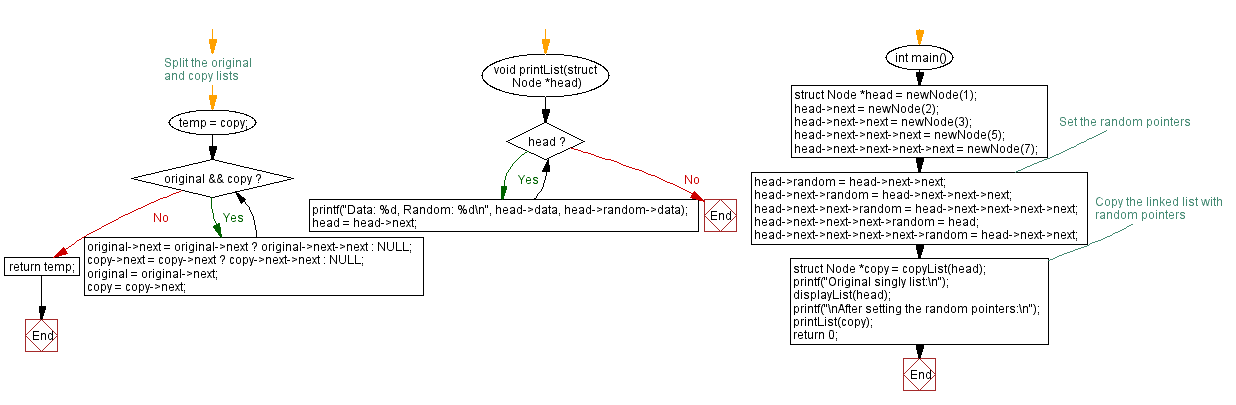
// Split the original and copy lists
temp = copy;
while (original && copy) {
original->next = original->next ? original->next->next : NULL;
copy->next = copy->next ? copy->next->next : NULL;
original = original->next;
copy = copy->next;
}
return temp; // Return the head of the copied list
}
// Function to print the elements and their corresponding random nodes in a linked list
void printList(struct Node *head) {
while (head) {
printf("Data: %d, Random: %d\n", head->data, head->random->data);
head = head->next;
}
}
// Main function where the execution starts
int main() {
// Create a singly linked list with nodes and random pointers
struct Node *head = newNode(1);
head->next = newNode(2);
head->next->next = newNode(3);
head->next->next->next = newNode(5);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(7);
// Set the random pointers for some nodes in the list
head->random = head->next->next;
head->next->random = head->next->next->next;
head->next->next->random = head->next->next->next->next;
head->next->next->next->random = head;
head->next->next->next->next->random = head->next->next;
// Copy the linked list with random pointers
struct Node *copy = copyList(head);
printf("Original singly list:\n");
displayList(head); // Display the original list
printf("\nAfter setting the random pointers:\n");
printList(copy); // Display the copied list with random pointers
return 0; // Indicates successful completion of the program
}
Sample Output:
Original singly list: 1 2 3 5 7 After setting the random pointers: Data: 1, Random: 3 Data: 2, Random: 5 Data: 3, Random: 7 Data: 5, Random: 1 Data: 7, Random: 3
Flowchart :
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to create a deep copy of a singly linked list with random pointers using a hash map.
- Write a C program to clone a linked list with random pointers by interweaving the original and copied nodes, then separating them.
- Write a C program to copy a linked list with random pointers and then swap the random pointers between the original and the copy.
- Write a C program to copy a linked list with random pointers and verify the integrity of the copied random links.
Go to:
PREV : Linked List Sorting Challenges.
NEXT : Intersection Finder Variants
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
