C Exercises: Check if a singly linked list is palindrome or not
15. Palindrome Check Variants
Write a C program to check if a singly linked list is a palindrome or not.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// Node structure for the linked list
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// Function to create a new node
struct Node* newNode(int data) {
struct Node* node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = data;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
// Function to reverse a linked list
struct Node* reverseList(struct Node* head) {
struct Node* current = head;
struct Node* next = NULL;
struct Node* prev = NULL;
while (current) {
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
return prev;
}
// Function to check if a linked list is a palindrome
bool isPalindrome(struct Node* head) {
struct Node* slow = head;
struct Node* fast = head;
struct Node* prev_slow = head;
struct Node* midnode = NULL;
bool res = true;
// Find the middle node
while (fast && fast->next) {
fast = fast->next->next;
prev_slow = slow;
slow = slow->next;
}
// If the number of nodes is odd, skip the middle node
if (fast != NULL) {
midnode = slow;
slow = slow->next;
}
// Reverse the second half of the linked list
slow = reverseList(slow);
fast = head;
// Compare the first and second half of the linked list
while (slow != NULL) {
if (fast->data != slow->data) {
res = false;
break;
}
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
// Reverse the second half of the linked list again
slow = reverseList(slow);
// If the number of nodes is odd, set the next pointer of the middle node to NULL
if (midnode != NULL) {
prev_slow->next = midnode;
midnode->next = slow;
} else
prev_slow->next = slow;
return res;
}
// Function to print a linked list of integers
void displayList(struct Node* head) {
while (head) {
printf("%d ", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// Function to print a linked list of characters
void displayList_char(struct Node* head) {
while (head) {
printf("%c", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
// Example 1: Integer linked list
struct Node* head1 = newNode(1);
head1->next = newNode(2);
head1->next->next = newNode(3);
head1->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head1->next->next->next->next = newNode(5);
printf("Original Singly List:\n");
displayList(head1);
if (isPalindrome(head1))
printf("Linked list is a palindrome.\n");
else
printf("Linked list is not a palindrome.\n");
// Example 2: Integer palindrome linked list
struct Node* head2 = newNode(1);
head2->next = newNode(2);
head2->next->next = newNode(2);
head2->next->next->next = newNode(1);
printf("\nOriginal Singly List:\n");
displayList(head2);
if (isPalindrome(head2))
printf("Linked list is a palindrome.\n");
else
printf("Linked list is not a palindrome.\n");
// Example 3: Character palindrome linked list
struct Node* head3 = newNode('M');
head3->next = newNode('A');
head3->next->next = newNode('D');
head3->next->next->next = newNode('A');
head3->next->next->next->next = newNode('M');
printf("\nOriginal Singly List:\n");
displayList_char(head3);
if (isPalindrome(head3))
printf("Linked list is a palindrome.\n");
else
printf("Linked list is not a palindrome.\n");
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Original Singly List: 1 2 3 4 5 Linked list is not a palindrome. Original Singly List: 1 2 2 1 Linked list is a palindrome. Original Singly List: MADAM Linked list is a palindrome.
Flowchart :
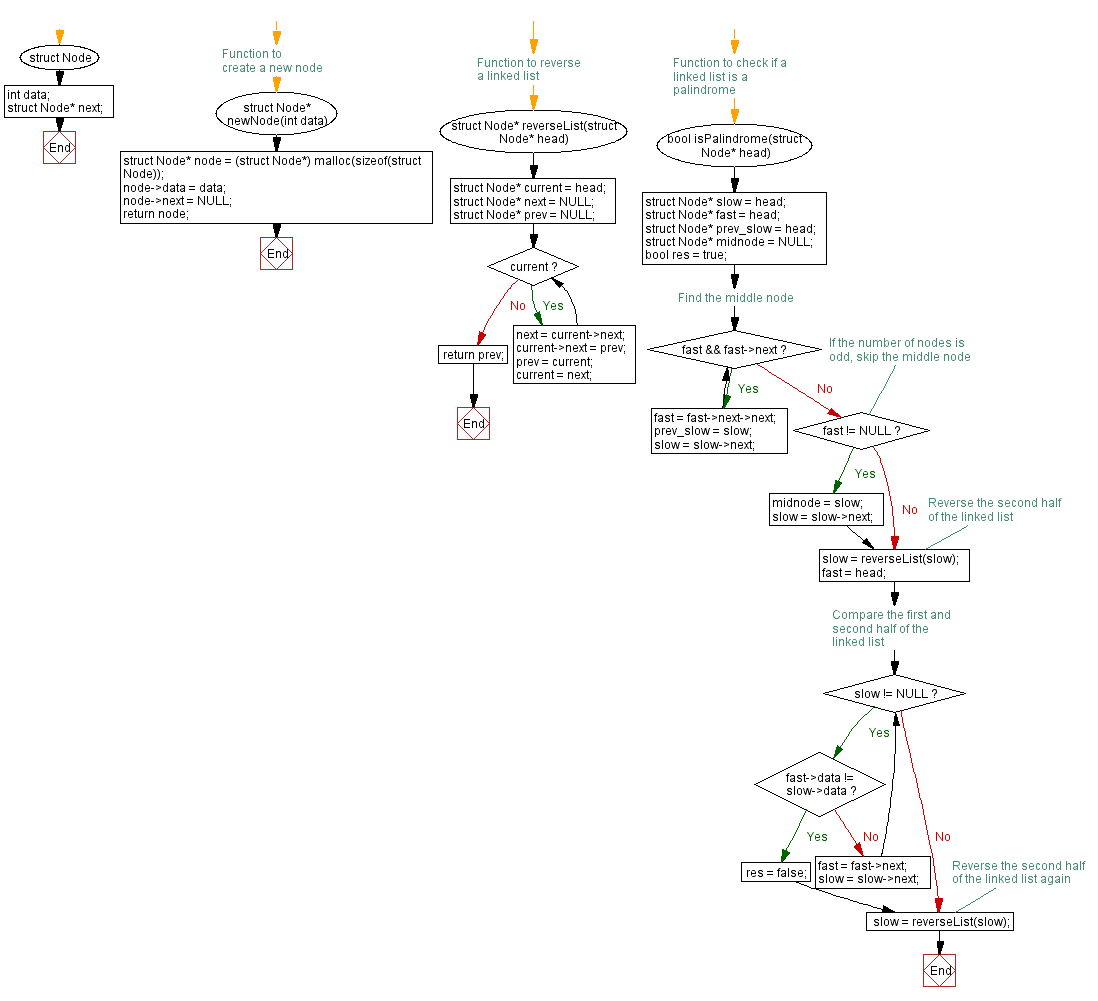
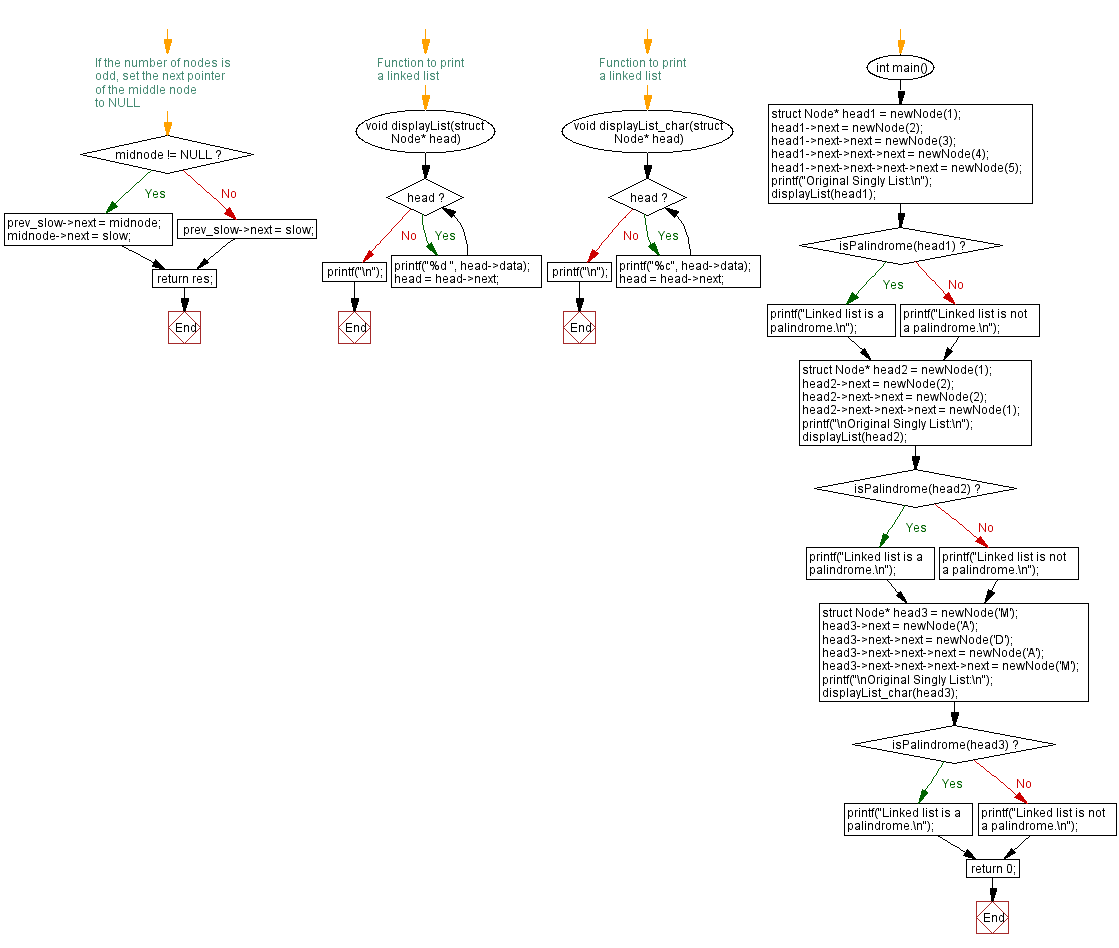
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to check if a singly linked list is a palindrome using a stack-based approach.
- Write a C program to recursively determine if a linked list of characters forms a palindrome.
- Write a C program to verify if a linked list is a palindrome by reversing its second half in place.
- Write a C program to check if a linked list containing case-sensitive characters is a palindrome.
Go to:
PREV : Loop Detection Challenges.
NEXT : Linked List Sorting Challenges.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
