C Exercises: Convert a Doubly Linked list into a string
21. Doubly Linked List to String Conversion
Write a C program to convert a Doubly Linked list into a string.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// Structure to define a doubly linked list node
struct node {
int num;
struct node *preptr;
struct node *nextptr;
}*stnode, *ennode;
// Function prototypes
void DlListcreation(int n);
void DlList_str();
int main() {
int n, num1, a, insPlc;
stnode = NULL;
ennode = NULL;
printf(" Input the number of nodes: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
// Function call to create a doubly linked list
DlListcreation(n);
// Function call to convert the doubly linked list to a string
DlList_str();
}
// Function to create a doubly linked list
void DlListcreation(int n) {
int i, num;
struct node *fnNode;
if (n >= 1) {
// Allocating memory for the first node
stnode = (struct node *) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (stnode != NULL) {
printf(" Input data for node 1 : "); // assigning data in the first node
scanf("%d", &num);
stnode->num = num;
stnode->preptr = NULL;
stnode->nextptr = NULL;
ennode = stnode;
// Loop to create subsequent nodes and link them in the list
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
fnNode = (struct node *) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (fnNode != NULL) {
printf(" Input data for node %d : ", i);
scanf("%d", &num);
fnNode->num = num;
fnNode->preptr = ennode; // new node is linking with the previous node
fnNode->nextptr = NULL; // set next address of fnnode is NULL
ennode->nextptr = fnNode; // previous node is linking with the new node
ennode = fnNode; // assign new node as the last node
} else {
printf(" Memory can not be allocated.");
break;
}
}
} else {
printf(" Memory can not be allocated.");
}
}
}
// Function to convert the doubly linked list to a string
void DlList_str() {
struct node *current;
current = stnode;
char text_str[100] = "";
// Loop through the list and concatenate node data to a string
while (current != NULL) {
char str[10];
sprintf(str, "%d", current->num);
strcat(text_str, str);
strcat(text_str, " ");
current = current->nextptr;
}
// Display the doubly linked list in string format
printf("\nThe doubly linked list in string format: %s\n", text_str);
}
Sample Output:
Input the number of nodes: 4 Input data for node 1 : 10 Input data for node 2 : 11 Input data for node 3 : 12 Input data for node 4 : 13 The doubly linked list in string format: 10 11 12 13
Flowchart :
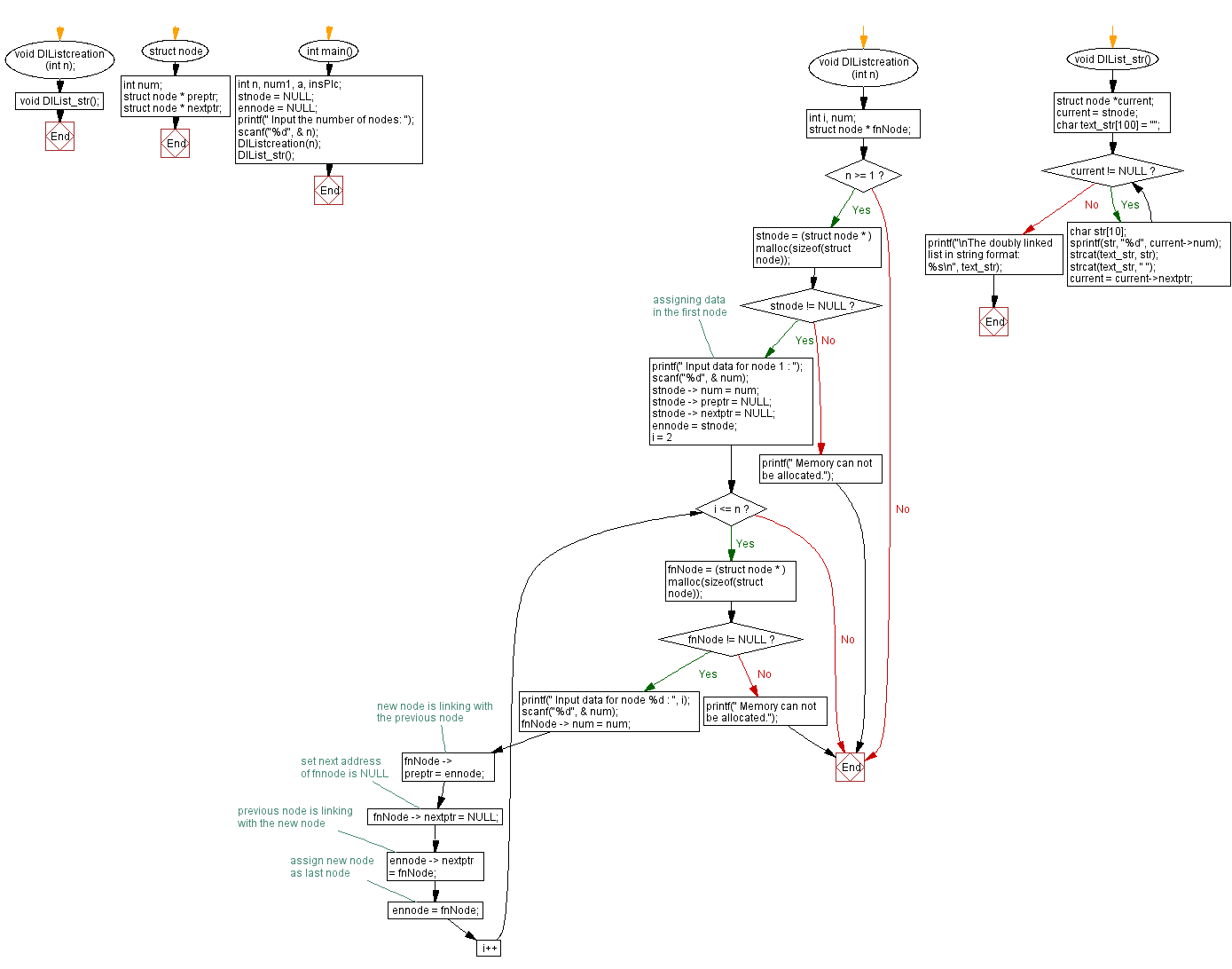
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to convert a doubly linked list into a comma-separated string representation.
- Write a C program to convert a doubly linked list into a string with each node value enclosed in square brackets.
- Write a C program to recursively convert a doubly linked list into a string and then reverse the string.
- Write a C program to convert a doubly linked list into a space-delimited string and count the total number of characters.
Go to:
PREV : Bubble Sort on Linked List.
NEXT : Doubly Linked List to Array Conversion.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
