C Exercises: Insert a node at the end of a circular linked list
14. Insert at End of Circular Linked List
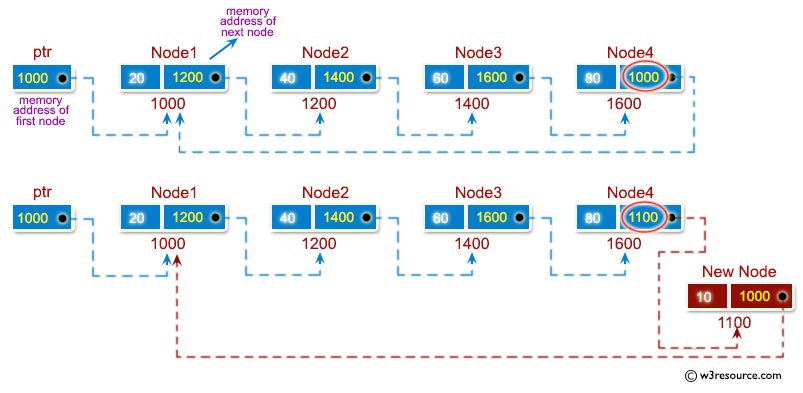
Write a program in C to insert a node at the end of a circular linked list.
Visual Presentation:
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include
#include
// Structure definition for a node in a circular linked list
struct node {
int num;
struct node *nextptr;
} *stnode; // Global pointer to the start of the circular linked list
// Function prototypes
void ClListcreation(int n);
void ClLinsertNodeAtEnd(int num);
void displayClList(int a);
int main() {
int n, num1, a;
stnode = NULL; // Initializing the start pointer of the circular list to NULL
printf("\n\n Circular Linked List: Insert a node at the end of a circular linked list :\n");
printf("--------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf(" Input the number of nodes : ");
scanf("%d", &n);
// Creating a circular linked list
ClListcreation(n);
a = 1; // Flag to display the initial list
displayClList(a);
printf(" Input the data to be inserted : ");
scanf("%d", &num1);
// Inserting a node at the end of the circular linked list
ClLinsertNodeAtEnd(num1);
a = 2; // Flag to display the list after insertion
displayClList(a);
return 0;
}
// Function to create a circular linked list
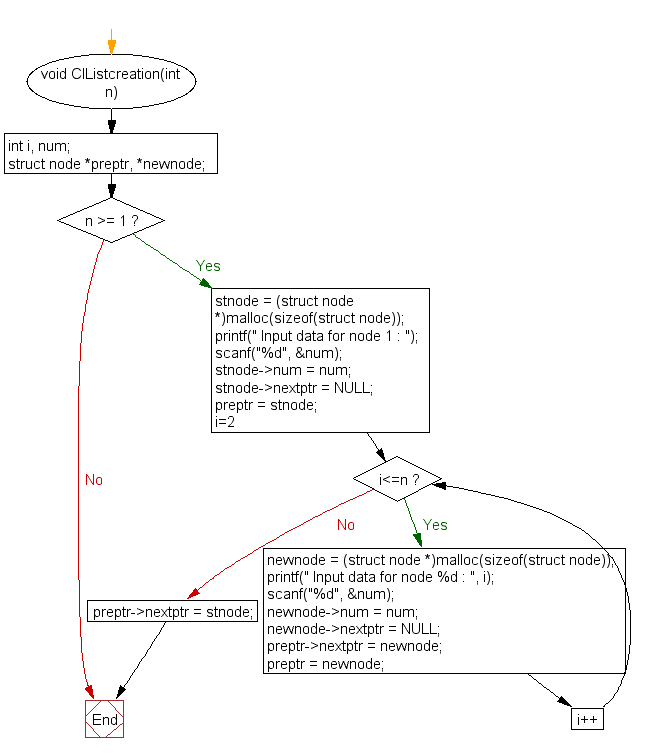
void ClListcreation(int n) {
int i, num;
struct node *preptr, *newnode;
if (n >= 1) {
// Allocating memory for the first node and initializing it
stnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
printf(" Input data for node 1 : ");
scanf("%d", &num);
stnode->num = num;
stnode->nextptr = NULL;
preptr = stnode;
// Loop to create subsequent nodes and link them to form a circular list
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
newnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
printf(" Input data for node %d : ", i);
scanf("%d", &num);
newnode->num = num;
newnode->nextptr = NULL;
preptr->nextptr = newnode;
preptr = newnode;
}
preptr->nextptr = stnode; // Linking the last node with the first node to form a circular list
}
}
// Function to insert a node at the end of the circular linked list
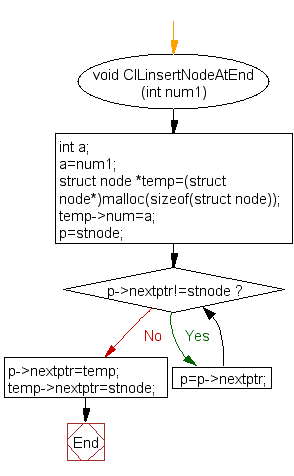
void ClLinsertNodeAtEnd(int num1) {
int a = num1;
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->num = a;
struct node *p = stnode; // Declaring 'p' to iterate through the list
// Loop to find the last node in the circular list
while (p->nextptr != stnode) {
p = p->nextptr;
}
p->nextptr = temp;
temp->nextptr = stnode;
}
// Function to display the circular linked list
void displayClList(int m) {
struct node *tmp;
int n = 1;
if (stnode == NULL) {
printf(" No data found in the List yet.");
} else {
tmp = stnode;
if (m == 1) {
printf("\n Data entered in the list are :\n");
} else {
printf("\n After insertion the new list are :\n");
}
// Loop to display nodes in the circular list
do {
printf(" Data %d = %d\n", n, tmp->num);
tmp = tmp->nextptr;
n++;
} while (tmp != stnode);
}
}
Sample Output:
Circular Linked List : Insert a node at the end of a circular linked list :
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Input the number of nodes : 3
Input data for node 1 : 2
Input data for node 2 : 5
Input data for node 3 : 8
Data entered in the list are :
Data 1 = 2
Data 2 = 5
Data 3 = 8
Input the data to be inserted : 9
After insertion the new list are :
Data 1 = 2
Data 2 = 5
Data 3 = 8
Data 4 = 9
Flowchart:
ClListcreation() :
ClLinsertNodeAtEnd() :
displayClList() :
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to append a node at the end of a circular linked list while ensuring the circular linkage remains intact.
- Write a C program to insert a node at the end of a circular linked list and then traverse the list to verify the insertion.
- Write a C program to add a node at the end of a circular linked list using a tail pointer for improved efficiency.
- Write a C program to append a node at the end of a circular linked list only if its value exceeds that of the current last node.
Go to:
PREV : Insert at Beginning of Circular Linked List.
NEXT : Insert at Any Position in Circular Linked List.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
