C Program: Basic Heap Operations - Insert, Delete, Display
1. Basic Heap Operations Extended Challenges
Write a C program that implements the basic operations of a heap - insert, delete, and display.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
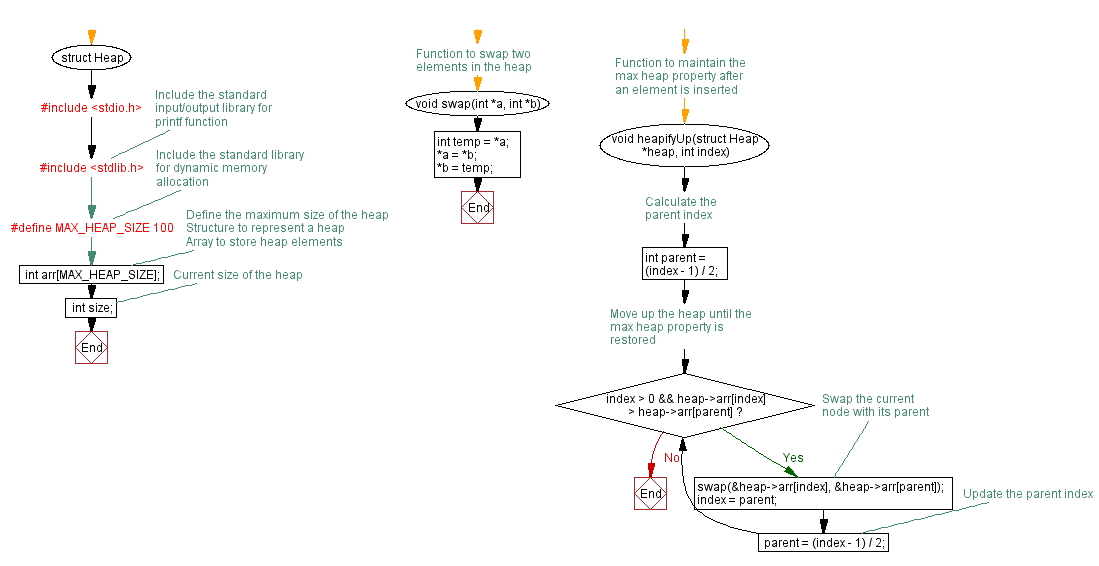
#include <stdio.h> // Include the standard input/output library for printf function
#include <stdlib.h> // Include the standard library for dynamic memory allocation
#define MAX_HEAP_SIZE 100 // Define the maximum size of the heap
// Structure to represent a heap
struct Heap {
int arr[MAX_HEAP_SIZE]; // Array to store heap elements
int size; // Current size of the heap
};
// Function to swap two elements in the heap
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// Function to maintain the max heap property after an element is inserted
void heapifyUp(struct Heap *heap, int index) {
int parent = (index - 1) / 2; // Calculate the parent index
// Move up the heap until the max heap property is restored
while (index > 0 && heap->arr[index] > heap->arr[parent]) {
swap(&heap->arr[index], &heap->arr[parent]); // Swap the current node with its parent
index = parent;
parent = (index - 1) / 2; // Update the parent index
}
}
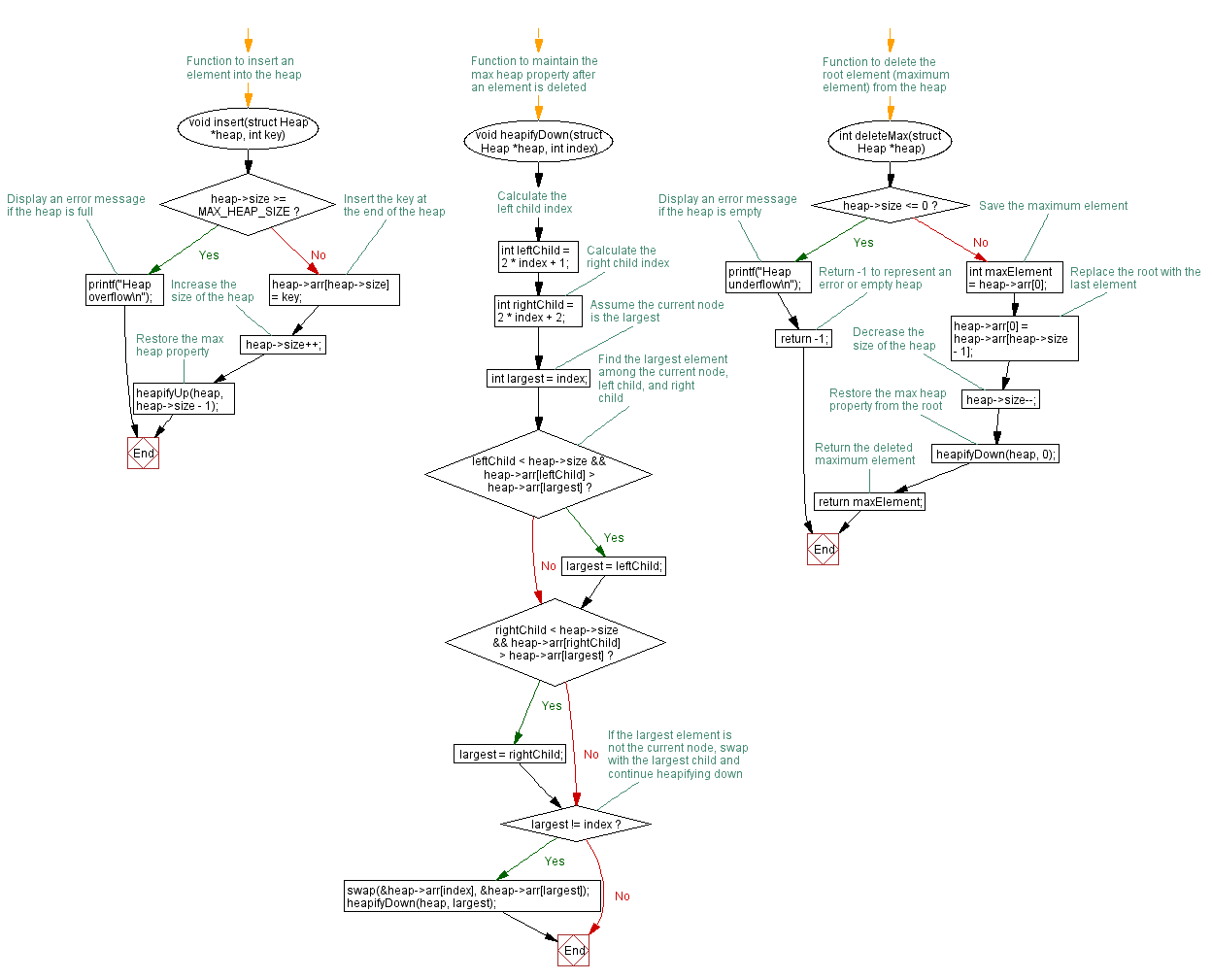
// Function to insert an element into the heap
void insert(struct Heap *heap, int key) {
if (heap->size >= MAX_HEAP_SIZE) {
printf("Heap overflow\n"); // Display an error message if the heap is full
return;
}
heap->arr[heap->size] = key; // Insert the key at the end of the heap
heap->size++; // Increase the size of the heap
heapifyUp(heap, heap->size - 1); // Restore the max heap property
}
// Function to maintain the max heap property after an element is deleted
void heapifyDown(struct Heap *heap, int index) {
int leftChild = 2 * index + 1; // Calculate the left child index
int rightChild = 2 * index + 2; // Calculate the right child index
int largest = index; // Assume the current node is the largest
// Find the largest element among the current node, left child, and right child
if (leftChild < heap->size && heap->arr[leftChild] > heap->arr[largest]) {
largest = leftChild;
}
if (rightChild < heap->size && heap->arr[rightChild] > heap->arr[largest]) {
largest = rightChild;
}
// If the largest element is not the current node, swap with the largest child and continue heapifying down
if (largest != index) {
swap(&heap->arr[index], &heap->arr[largest]);
heapifyDown(heap, largest);
}
}
// Function to delete the root element (maximum element) from the heap
int deleteMax(struct Heap *heap) {
if (heap->size <= 0) {
printf("Heap underflow\n"); // Display an error message if the heap is empty
return -1; // Return -1 to represent an error or empty heap
}
int maxElement = heap->arr[0]; // Save the maximum element
heap->arr[0] = heap->arr[heap->size - 1]; // Replace the root with the last element
heap->size--; // Decrease the size of the heap
heapifyDown(heap, 0); // Restore the max heap property from the root
return maxElement; // Return the deleted maximum element
}
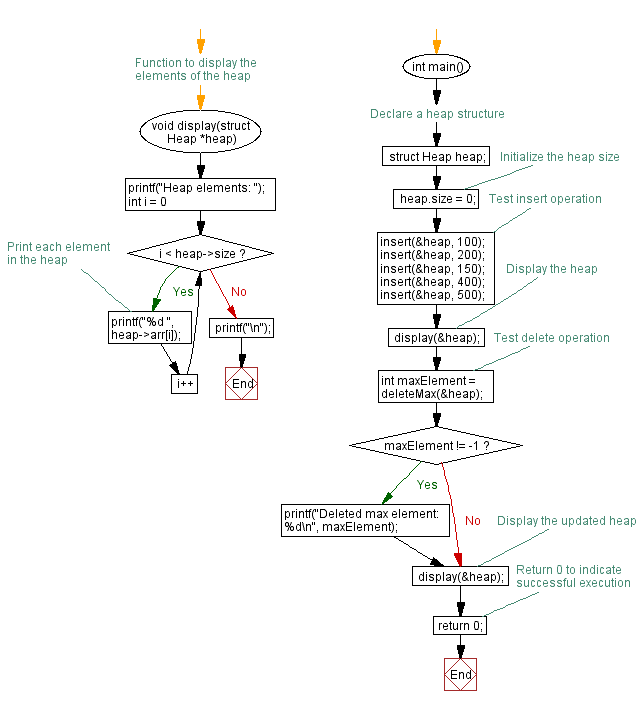
// Function to display the elements of the heap
void display(struct Heap *heap) {
printf("Heap elements: ");
for (int i = 0; i < heap->size; i++) {
printf("%d ", heap->arr[i]); // Print each element in the heap
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
struct Heap heap; // Declare a heap structure
heap.size = 0; // Initialize the heap size
// Test insert operation
insert(&heap, 100);
insert(&heap, 200);
insert(&heap, 150);
insert(&heap, 400);
insert(&heap, 500);
// Display the heap
display(&heap);
// Test delete operation
int maxElement = deleteMax(&heap);
if (maxElement != -1) {
printf("Deleted max element: %d\n", maxElement);
}
// Display the updated heap
display(&heap);
return 0; // Return 0 to indicate successful execution
}
Output:
Heap elements: 500 400 150 100 200 Deleted max element: 500 Heap elements: 400 200 150 100
Explanation:
In the exercise above -
- Header and definitions:
- The code includes standard input/output and standard library headers.
- It defines a constant MAX_HEAP_SIZE for the maximum size of the heap.
- Heap Structure:
- Declares a structure Heap to represent a max heap.
- The structure contains an array to store heap elements (arr) and the current size of the heap (size).
- Swap Function:
- Define a swap function to exchange the values of two variables.
- Heapify Up Function:
- Implement heapifyUp to maintain the max heap property after inserting an element.
- Ensure the newly inserted element is moved up the heap to its correct position.
- Insert Function:
- Implement insert to add an element to the heap.
- Checks for heap overflow and then inserts the element, followed by calling heapifyUp.
- Heapify Down Function:
- Define heapifyDown to maintain the max heap property after deleting an element.
- Ensure the heap property is maintained by moving the larger child up.
- DeleteMax Function:
- Implement deleteMax to remove the maximum element (root) from the heap.
- Checks for heap underflow, replaces the root with the last element, and calls heapifyDown.
- Display Function:
- Implements display to print the elements of the heap.
- Main Function:
- Declares a Heap structure and initializes its size to 0.
- Tests the insert operation with some values and displays the heap.
- Tests the delete operation (deleteMax) and displays the updated heap.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to implement a dynamic heap that auto-resizes and supports both insert and delete operations in O(log n) time.
- Write a C program to implement a heap storing custom structures with function pointers for custom comparison logic.
- Write a C program to implement a heap with comprehensive error handling for memory allocation failures and underflow/overflow conditions.
- Write a C program to simulate a binary heap using pointer arithmetic instead of array indexing.
Go to:
PREV :C Programming Heap Exercises and Solutions Home
NEXT : Construct Max Heap Extended Challenges.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
