C Program: Collision Resolution Performance Analysis
8. Collision Resolution Performance Comparison Challenges
Write a C program that compares the performance of different collision resolution methods (chaining, linear probing, etc.) in terms of speed and memory usage.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
// Including necessary header files
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <chrono>
#define TABLE_SIZE 10000
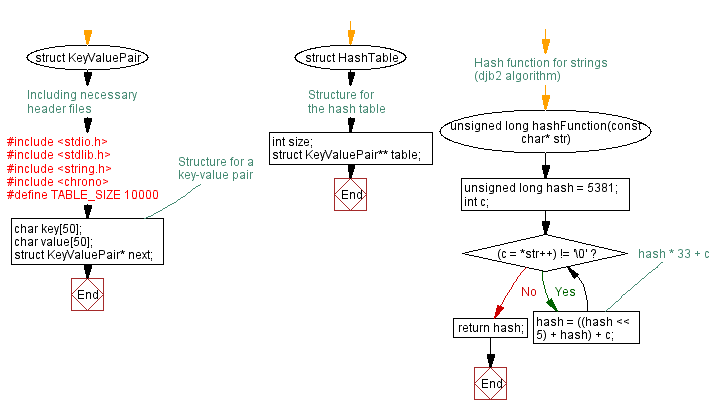
// Structure for a key-value pair
struct KeyValuePair {
char key[50];
char value[50];
struct KeyValuePair* next;
};
// Structure for the hash table
struct HashTable {
int size;
struct KeyValuePair** table;
};
// Hash function for strings (djb2 algorithm)
unsigned long hashFunction(const char* str) {
unsigned long hash = 5381;
int c;
while ((c = *str++) != '\0') {
hash = ((hash << 5) + hash) + c; // hash * 33 + c
}
return hash;
}
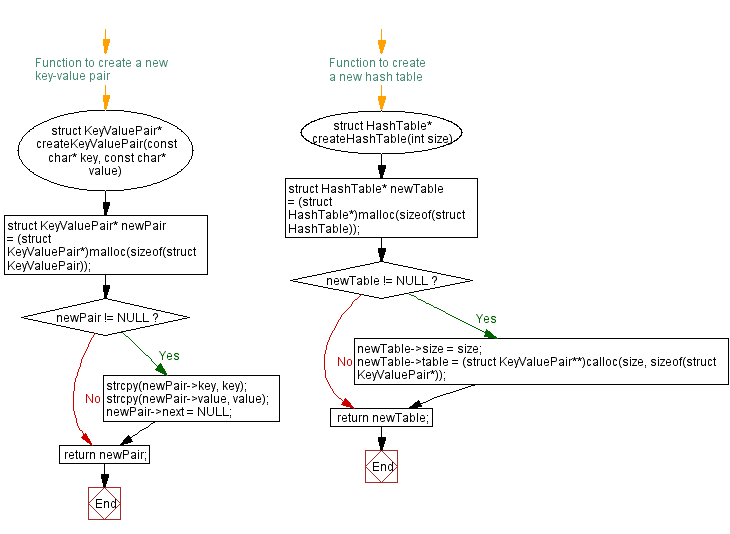
// Function to create a new key-value pair
struct KeyValuePair* createKeyValuePair(const char* key, const char* value) {
struct KeyValuePair* newPair = (struct KeyValuePair*)malloc(sizeof(struct KeyValuePair));
if (newPair != NULL) {
strcpy(newPair->key, key);
strcpy(newPair->value, value);
newPair->next = NULL;
}
return newPair;
}
// Function to create a new hash table
struct HashTable* createHashTable(int size) {
struct HashTable* newTable = (struct HashTable*)malloc(sizeof(struct HashTable));
if (newTable != NULL) {
newTable->size = size;
newTable->table = (struct KeyValuePair**)calloc(size, sizeof(struct KeyValuePair*));
}
return newTable;
}
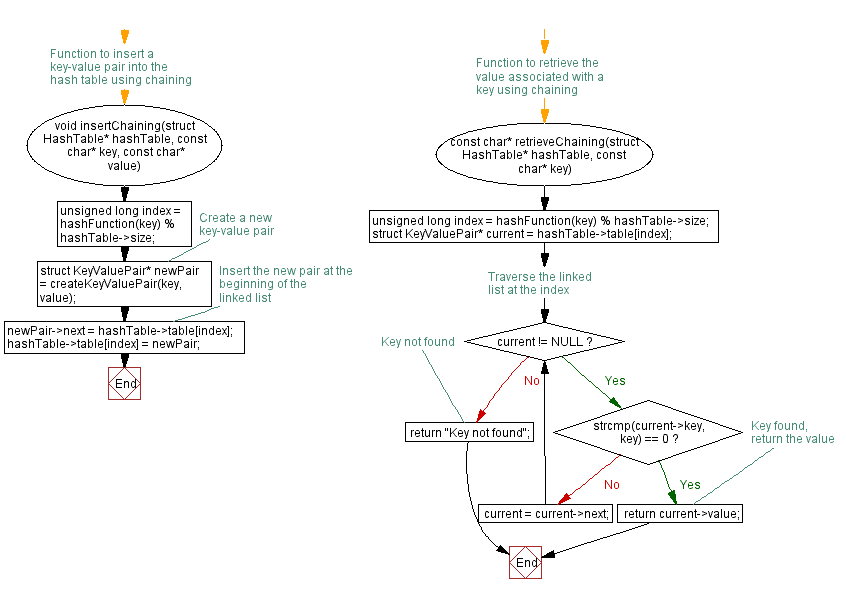
// Function to insert a key-value pair into the hash table using chaining
void insertChaining(struct HashTable* hashTable, const char* key, const char* value) {
unsigned long index = hashFunction(key) % hashTable->size;
// Create a new key-value pair
struct KeyValuePair* newPair = createKeyValuePair(key, value);
// Insert the new pair at the beginning of the linked list
newPair->next = hashTable->table[index];
hashTable->table[index] = newPair;
}
// Function to retrieve the value associated with a key using chaining
const char* retrieveChaining(struct HashTable* hashTable, const char* key) {
unsigned long index = hashFunction(key) % hashTable->size;
struct KeyValuePair* current = hashTable->table[index];
// Traverse the linked list at the index
while (current != NULL) {
if (strcmp(current->key, key) == 0) {
return current->value; // Key found, return the value
}
current = current->next;
}
return "Key not found"; // Key not found
}
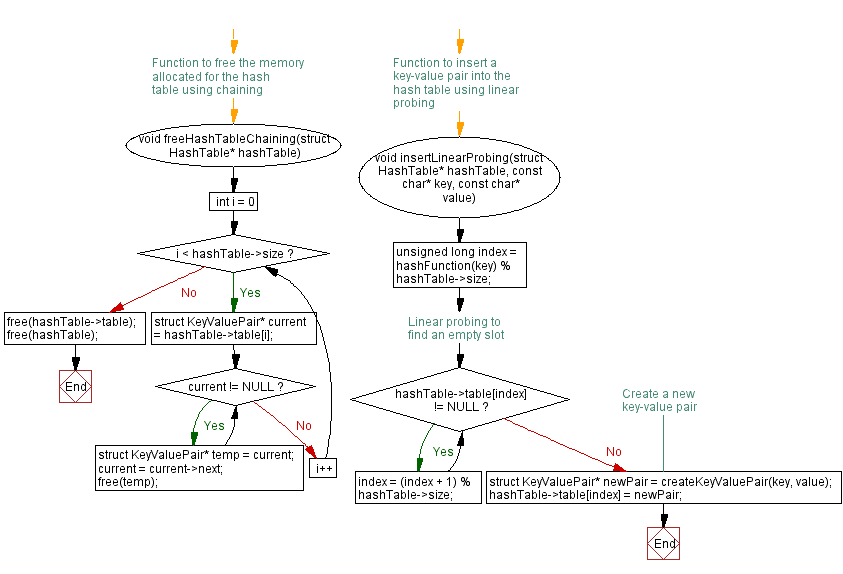
// Function to free the memory allocated for the hash table using chaining
void freeHashTableChaining(struct HashTable* hashTable) {
for (int i = 0; i < hashTable->size; i++) {
struct KeyValuePair* current = hashTable->table[i];
while (current != NULL) {
struct KeyValuePair* temp = current;
current = current->next;
free(temp);
}
}
free(hashTable->table);
free(hashTable);
}
// Function to insert a key-value pair into the hash table using linear probing
void insertLinearProbing(struct HashTable* hashTable, const char* key, const char* value) {
unsigned long index = hashFunction(key) % hashTable->size;
// Linear probing to find an empty slot
while (hashTable->table[index] != NULL) {
index = (index + 1) % hashTable->size;
}
// Create a new key-value pair
struct KeyValuePair* newPair = createKeyValuePair(key, value);
hashTable->table[index] = newPair;
}
// Function to retrieve the value associated with a key using linear probing
const char* retrieveLinearProbing(struct HashTable* hashTable, const char* key) {
unsigned long index = hashFunction(key) % hashTable->size;
// Linear probing to find the key
while (hashTable->table[index] != NULL) {
if (strcmp(hashTable->table[index]->key, key) == 0) {
return hashTable->table[index]->value; // Key found, return the value
}
index = (index + 1) % hashTable->size;
}
return "Key not found"; // Key not found
}
// Function to free the memory allocated for the hash table using linear probing
void freeHashTableLinearProbing(struct HashTable* hashTable) {
for (int i = 0; i < hashTable->size; i++) {
free(hashTable->table[i]);
}
free(hashTable->table);
free(hashTable);
}
// Function to perform performance testing with chaining
void testChaining() {
struct HashTable* hashTable = createHashTable(TABLE_SIZE);
// Insert key-value pairs
for (int i = 0; i < TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
char key[50];
char value[50];
sprintf(key, "Key%d", i);
sprintf(value, "Value%d", i);
insertChaining(hashTable, key, value);
}
// Retrieve key-value pairs
for (int i = 0; i < TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
char key[50];
sprintf(key, "Key%d", i);
const char* result = retrieveChaining(hashTable, key);
printf("Chaining - Retrieved value for key '%s': %s\n", key, result);
}
// Free allocated memory
freeHashTableChaining(hashTable);
}
// Function to perform performance testing with linear probing
void testLinearProbing() {
struct HashTable* hashTable = createHashTable(TABLE_SIZE);
// Insert key-value pairs
for (int i = 0; i < TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
char key[50];
char value[50];
sprintf(key, "Key%d", i);
sprintf(value, "Value%d", i);
insertLinearProbing(hashTable, key, value);
}
// Retrieve key-value pairs
for (int i = 0; i < TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
char key[50];
sprintf(key, "Key%d", i);
const char* result = retrieveLinearProbing(hashTable, key);
printf("Linear Probing - Retrieved value for key '%s': %s\n", key, result);
}
// Free allocated memory
freeHashTableLinearProbing(hashTable);
}
int main() {
// Perform performance testing with chaining
auto startChaining = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
testChaining();
auto endChaining = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto durationChaining = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(endChaining - startChaining);
// Perform performance testing with linear probing
auto startLinearProbing = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
testLinearProbing();
auto endLinearProbing = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto durationLinearProbing = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(endLinearProbing - startLinearProbing);
// Print performance results
printf("\nPerformance Results:\n");
printf("Chaining Duration: %lld microseconds\n", durationChaining.count());
printf("Linear Probing Duration: %lld microseconds\n", durationLinearProbing.count());
return 0;
}
Output:
Linear Probing - Retrieved value for key 'Key1007': Value1007 Linear Probing - Retrieved value for key 'Key1008': Value1008 Linear Probing - Retrieved value for key 'Key1009': Value1009 Linear Probing - Retrieved value for key 'Key1010': Value1010 Linear Probing - Retrieved value for key 'Key1011': Value1011 Linear Probing - Retrieved value for key 'Key1012': Value1012 Linear Probing - Retrieved value for key 'Key1013': Value1013 Linear Probing - Retrieved value for key 'Key1014': Value1014 Linear Probing - Retrieved value for key 'Key1015': Value1015 Linear Probing - Retrieved value for key 'Key1016': Value1016 Linear Probing - Retrieved value for key 'Key1017': Value1017 Linear Probing - Retrieved value for key 'Key1018': Value1018 Linear Probing - Retrieved value for key 'Key1019': Value1019 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Explanation:
In the exercise above,
- Hash table structure:
- The program defines a structure 'KeyValuePair' for a key-value pair and a structure 'HashTable' for a hash table.
- The hash table uses an array of pointers to 'KeyValuePair' structures (struct KeyValuePair** table).
- Hash function:
- The hashFunction is a simple hash function (djb2 algorithm) that generates a hash value for a given string.
- Key-Value Pair Creation:
- The createKeyValuePair function dynamically allocates memory for a new key-value pair and initializes its fields.
- Hash table creation:
- The createHashTable function dynamically allocates memory for a new hash table and initializes its fields.
- Chaining Operations:
- insertChaining: Inserts a key-value pair into the hash table using chaining.
- retrieveChaining: Retrieves the value associated with a key using chaining.
- freeHashTableChaining: Frees the memory allocated for the hash table using chaining.
- Linear probing operations:
- insertLinearProbing: Inserts a key-value pair into the hash table using linear probing.
- retrieveLinearProbing: Retrieves the value associated with a key using linear probing.
- freeHashTableLinearProbing: Frees the memory allocated for the hash table using linear probing.
- Performance testing:
- The testChaining and testLinearProbing functions perform performance testing for chaining and linear probing, respectively.
- Key-value pairs are inserted into the hash table, and then retrieval operations are performed.
- Main functions:
- The "main()" function measures the duration of the chaining and linear probing tests using the
library for timing. - The program prints the duration of each test, providing insights into the performance of the two collision resolution methods.
Flowchart
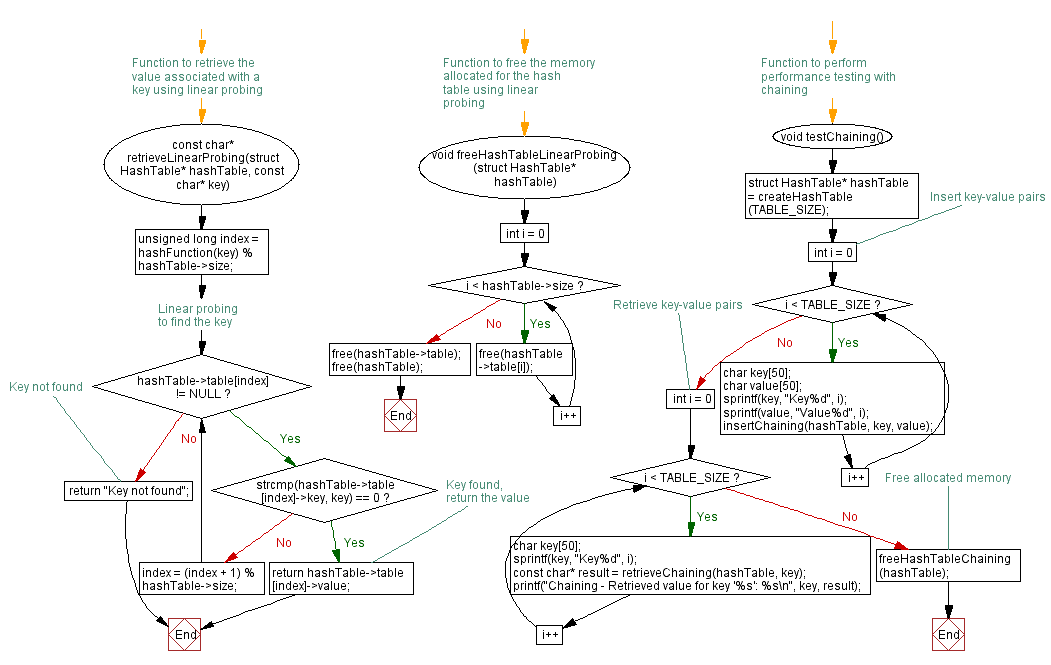
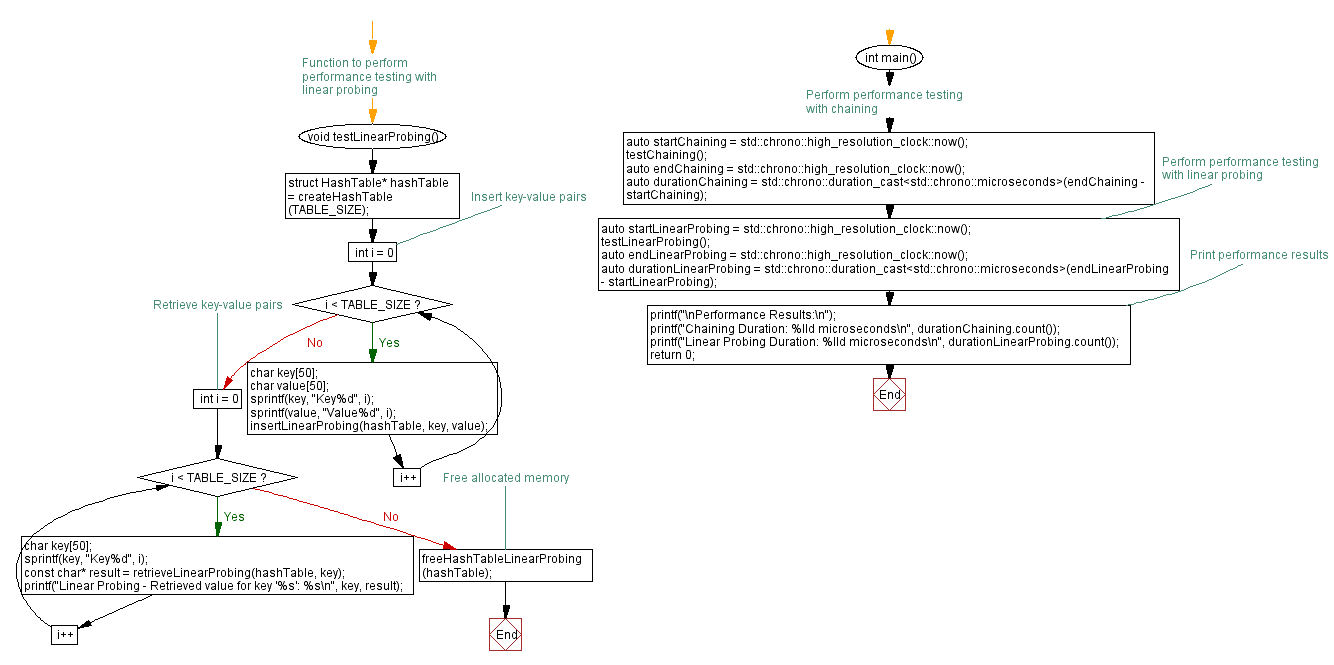
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to benchmark and compare insertion times for hash tables using chaining and linear probing.
- Write a C program to measure memory usage differences between open addressing and chaining in hash table implementations.
- Write a C program to calculate the average number of probes per insertion for various collision resolution methods.
- Write a C program to simulate high load factor scenarios and compare the performance of different collision resolution techniques.
Go to:
PREV : Open Addressing Techniques Challenges.
NEXT : Generic Hash Table Challenges.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
