C Program: String Hash function and Hash table
3. String Hash Function Challenges
Write a C program that creates a hash function specifically designed for strings and implements a hash table to store and retrieve string data.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
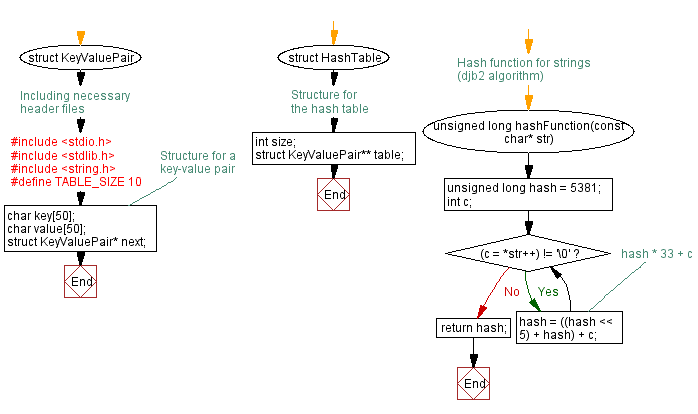
// Including necessary header files
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define TABLE_SIZE 10
// Structure for a key-value pair
struct KeyValuePair {
char key[50];
char value[50];
struct KeyValuePair* next;
};
// Structure for the hash table
struct HashTable {
int size;
struct KeyValuePair** table;
};
// Hash function for strings (djb2 algorithm)
unsigned long hashFunction(const char* str) {
unsigned long hash = 5381;
int c;
while ((c = *str++) != '\0') {
hash = ((hash << 5) + hash) + c; // hash * 33 + c
}
return hash;
}
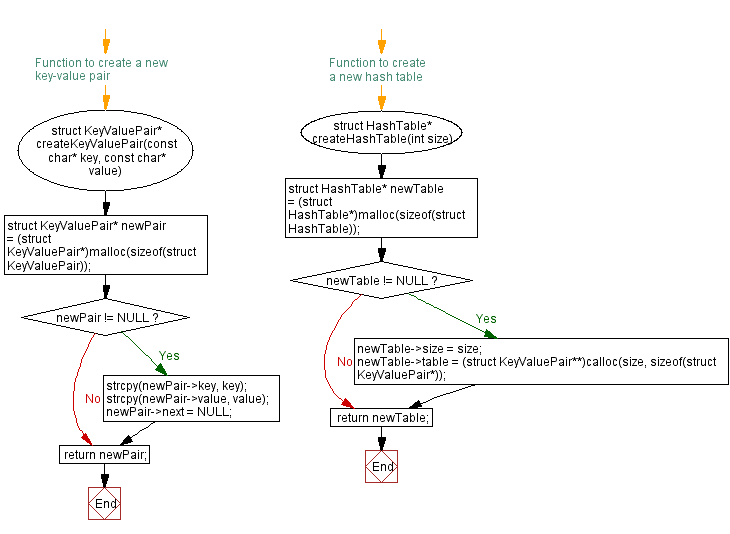
// Function to create a new key-value pair
struct KeyValuePair* createKeyValuePair(const char* key, const char* value) {
struct KeyValuePair* newPair = (struct KeyValuePair*)malloc(sizeof(struct KeyValuePair));
if (newPair != NULL) {
strcpy(newPair->key, key);
strcpy(newPair->value, value);
newPair->next = NULL;
}
return newPair;
}
// Function to create a new hash table
struct HashTable* createHashTable(int size) {
struct HashTable* newTable = (struct HashTable*)malloc(sizeof(struct HashTable));
if (newTable != NULL) {
newTable->size = size;
newTable->table = (struct KeyValuePair**)calloc(size, sizeof(struct KeyValuePair*));
}
return newTable;
}
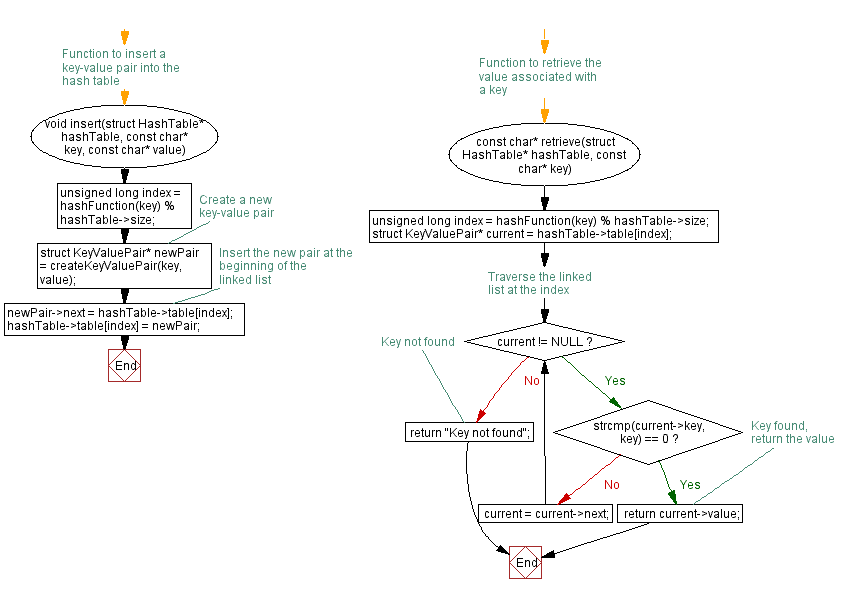
// Function to insert a key-value pair into the hash table
void insert(struct HashTable* hashTable, const char* key, const char* value) {
unsigned long index = hashFunction(key) % hashTable->size;
// Create a new key-value pair
struct KeyValuePair* newPair = createKeyValuePair(key, value);
// Insert the new pair at the beginning of the linked list
newPair->next = hashTable->table[index];
hashTable->table[index] = newPair;
}
// Function to retrieve the value associated with a key
const char* retrieve(struct HashTable* hashTable, const char* key) {
unsigned long index = hashFunction(key) % hashTable->size;
struct KeyValuePair* current = hashTable->table[index];
// Traverse the linked list at the index
while (current != NULL) {
if (strcmp(current->key, key) == 0) {
return current->value; // Key found, return the value
}
current = current->next;
}
return "Key not found"; // Key not found
}
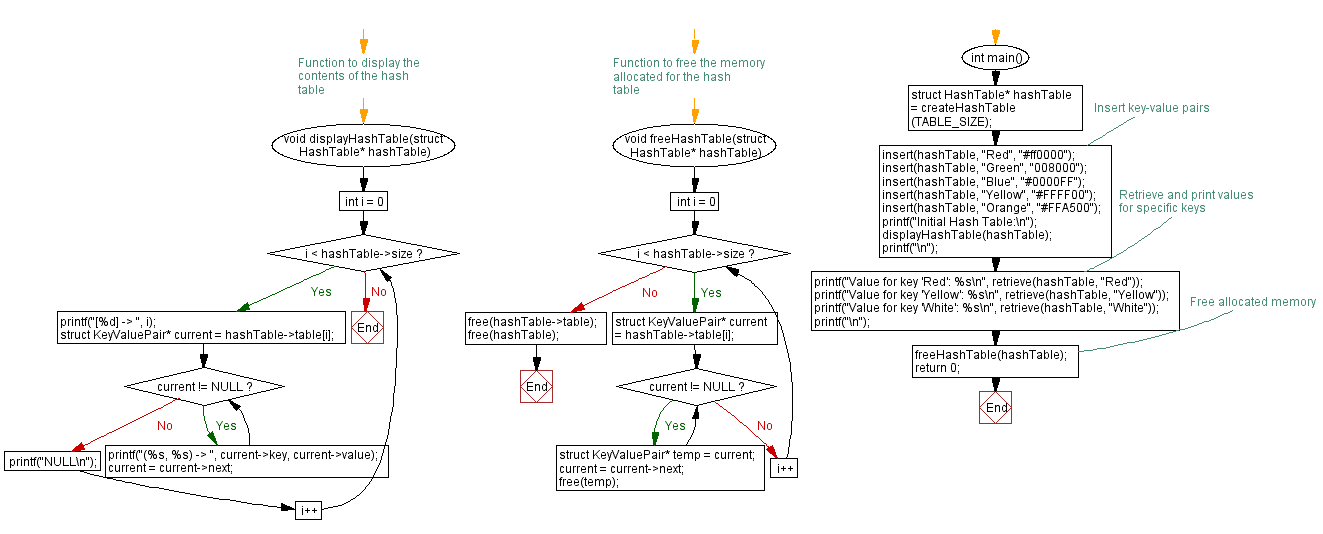
// Function to display the contents of the hash table
void displayHashTable(struct HashTable* hashTable) {
for (int i = 0; i < hashTable->size; i++) {
printf("[%d] -> ", i);
struct KeyValuePair* current = hashTable->table[i];
while (current != NULL) {
printf("(%s, %s) -> ", current->key, current->value);
current = current->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
}
// Function to free the memory allocated for the hash table
void freeHashTable(struct HashTable* hashTable) {
for (int i = 0; i < hashTable->size; i++) {
struct KeyValuePair* current = hashTable->table[i];
while (current != NULL) {
struct KeyValuePair* temp = current;
current = current->next;
free(temp);
}
}
free(hashTable->table);
free(hashTable);
}
int main() {
struct HashTable* hashTable = createHashTable(TABLE_SIZE);
// Insert key-value pairs
insert(hashTable, "Red", "#ff0000");
insert(hashTable, "Green", "008000");
insert(hashTable, "Blue", "#0000FF");
insert(hashTable, "Yellow", "#FFFF00");
insert(hashTable, "Orange", "#FFA500");
printf("Initial Hash Table:\n");
displayHashTable(hashTable);
printf("\n");
// Retrieve and print values for specific keys
printf("Value for key 'Red': %s\n", retrieve(hashTable, "Red"));
printf("Value for key 'Yellow': %s\n", retrieve(hashTable, "Yellow"));
printf("Value for key 'White': %s\n", retrieve(hashTable, "White"));
printf("\n");
// Free allocated memory
freeHashTable(hashTable);
return 0;
}
Output:
Initial Hash Table: [0] -> (Green, 008000) -> NULL [1] -> (Orange, #FFA500) -> (Blue, #0000FF) -> NULL [2] -> NULL [3] -> NULL [4] -> NULL [5] -> NULL [6] -> NULL [7] -> NULL [8] -> (Red, #ff0000) -> NULL [9] -> (Yellow, #FFFF00) -> NULL Value for key 'Red': #ff0000 Value for key 'Yellow': #FFFF00 Value for key 'White': Key not found
Explanation:
In the exercise above -
- Structures:
- KeyValuePair: Represents a key-value pair with strings for key and value, linked to handle collisions.
- HashTable: Represents the hash table with a size and an array of pointers to key-value pairs.
- Hash Function (hashFunction):
- Implements the djb2 hash algorithm to convert a string key into a hash value.
- Key-Value Pair Functions:
- createKeyValuePair: Allocates memory for a new key-value pair and initializes it with the provided key and value.
- Hash Table Functions:
- createHashTable: Allocates memory for a new hash table and initializes its size and array of pointers.
- insert: Inserts a key-value pair into the hash table using the hash function.
- retrieve: Retrieves the value associated with a given key from the hash table.
- displayHashTable: Displays the contents of the hash table, including linked lists for handling collisions.
- freeHashTable: Frees the memory allocated for the hash table.
- Main Function (main):
- Creates a hash table of a specified size (TABLE_SIZE).
- Inserts several key-value pairs into the hash table.
- Displays the initial hash table.
- Retrieves and prints values for specific keys.
- Frees the memory allocated for the hash table.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to implement a hash table for strings using a polynomial rolling hash function.
- Write a C program to design a case-insensitive string hash function and integrate it into a hash table.
- Write a C program to implement a hash table for long strings optimized with bitwise operations in the hash function.
- Write a C program to implement a hash table that supports Unicode string keys by adjusting the hash function accordingly.
Go to:
PREV : Collision Resolution Extension Challenges.
NEXT : Dynamic Resizing Challenges.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
