Creating a spell checker in C using Hash table
10. Hash Table Spell Checker Challenges
Write a C program that creates a hash table to implement a simple spell checker. Load a dictionary of words into the hash table and check the spelling of input words.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
// Including necessary header files
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define DICTIONARY_SIZE 1000
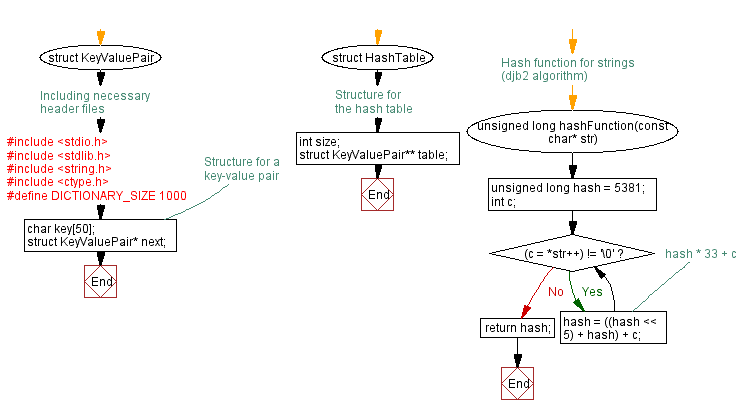
// Structure for a key-value pair
struct KeyValuePair {
char key[50];
struct KeyValuePair* next;
};
// Structure for the hash table
struct HashTable {
int size;
struct KeyValuePair** table;
};
// Hash function for strings (djb2 algorithm)
unsigned long hashFunction(const char* str) {
unsigned long hash = 5381;
int c;
while ((c = *str++) != '\0') {
hash = ((hash << 5) + hash) + c; // hash * 33 + c
}
return hash;
}
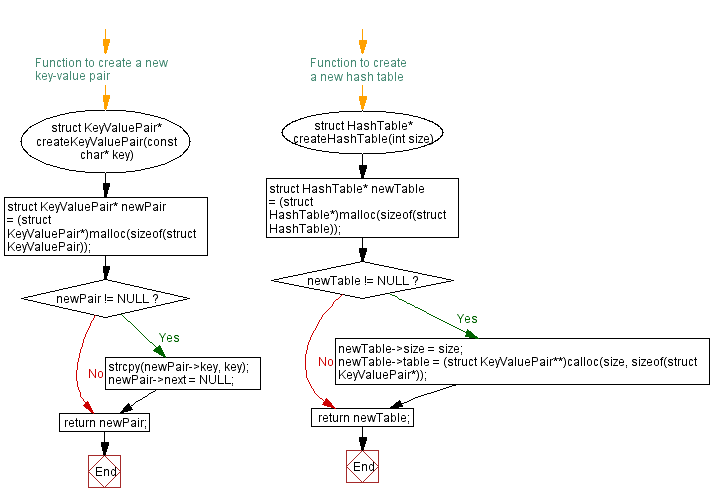
// Function to create a new key-value pair
struct KeyValuePair* createKeyValuePair(const char* key) {
struct KeyValuePair* newPair = (struct KeyValuePair*)malloc(sizeof(struct KeyValuePair));
if (newPair != NULL) {
strcpy(newPair->key, key);
newPair->next = NULL;
}
return newPair;
}
// Function to create a new hash table
struct HashTable* createHashTable(int size) {
struct HashTable* newTable = (struct HashTable*)malloc(sizeof(struct HashTable));
if (newTable != NULL) {
newTable->size = size;
newTable->table = (struct KeyValuePair**)calloc(size, sizeof(struct KeyValuePair*));
}
return newTable;
}
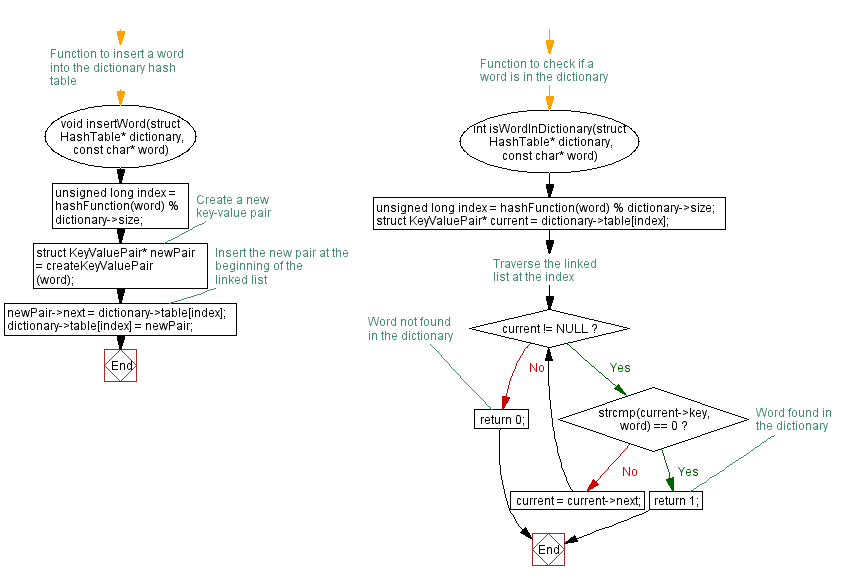
// Function to insert a word into the dictionary hash table
void insertWord(struct HashTable* dictionary, const char* word) {
unsigned long index = hashFunction(word) % dictionary->size;
// Create a new key-value pair
struct KeyValuePair* newPair = createKeyValuePair(word);
// Insert the new pair at the beginning of the linked list
newPair->next = dictionary->table[index];
dictionary->table[index] = newPair;
}
// Function to check if a word is in the dictionary
int isWordInDictionary(struct HashTable* dictionary, const char* word) {
unsigned long index = hashFunction(word) % dictionary->size;
struct KeyValuePair* current = dictionary->table[index];
// Traverse the linked list at the index
while (current != NULL) {
if (strcmp(current->key, word) == 0) {
return 1; // Word found in the dictionary
}
current = current->next;
}
return 0; // Word not found in the dictionary
}
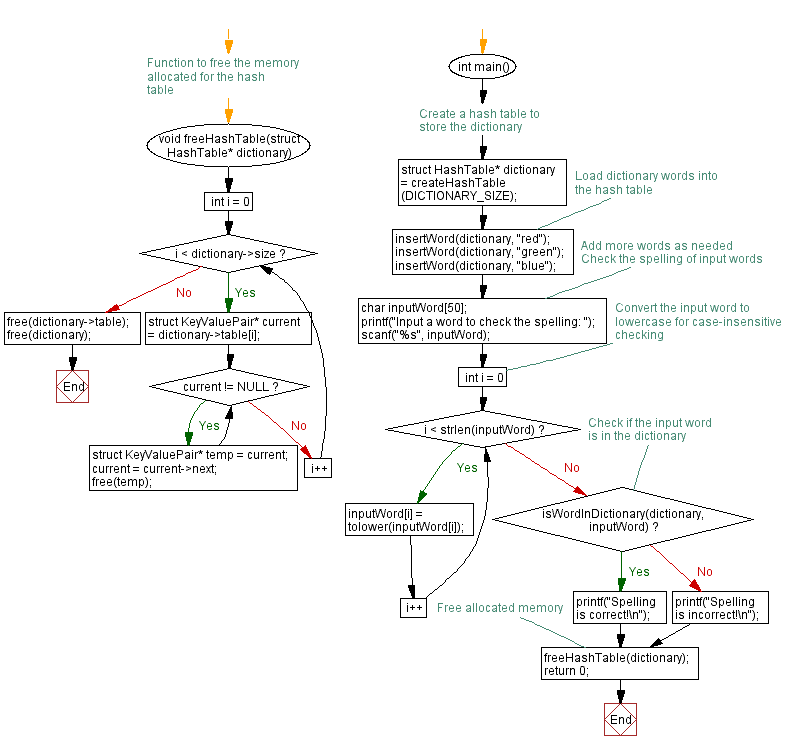
// Function to free the memory allocated for the hash table
void freeHashTable(struct HashTable* dictionary) {
for (int i = 0; i < dictionary->size; i++) {
struct KeyValuePair* current = dictionary->table[i];
while (current != NULL) {
struct KeyValuePair* temp = current;
current = current->next;
free(temp);
}
}
free(dictionary->table);
free(dictionary);
}
int main() {
// Create a hash table to store the dictionary
struct HashTable* dictionary = createHashTable(DICTIONARY_SIZE);
// Load dictionary words into the hash table
insertWord(dictionary, "red");
insertWord(dictionary, "green");
insertWord(dictionary, "blue");
// Add more words as needed
// Check the spelling of input words
char inputWord[50];
printf("Input a word to check the spelling: ");
scanf("%s", inputWord);
// Convert the input word to lowercase for case-insensitive checking
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(inputWord); i++) {
inputWord[i] = tolower(inputWord[i]);
}
// Check if the input word is in the dictionary
if (isWordInDictionary(dictionary, inputWord)) {
printf("Spelling is correct!\n");
} else {
printf("Spelling is incorrect!\n");
}
// Free allocated memory
freeHashTable(dictionary);
return 0;
}
Output:
Input a word to check the spelling: blua Spelling is incorrect!
Input a word to check the spelling: blue Spelling is correct!
Explanation:
In the exercise above,
- Header Files:
- stdio.h: Standard input/output functions.
- stdlib.h: Standard library functions, including memory allocation (malloc) and deallocation (free).
- string.h: String manipulation functions.
- ctype.h: Functions for character classification (e.g., "tolower()").
- Macros:
- DICTIONARY_SIZE: Defines the size of the hash table.
- Structures:
- KeyValuePair: Represents a key-value pair in the hash table, where the key is a word, and next is a pointer to the next KeyValuePair in case of collisions.
- HashTable: Represents the hash table, consisting of a size and an array of pointers to KeyValuePairs.
- Hash Function (hashFunction):
- Implements the djb2 algorithm to calculate the hash value for a given string.
- Functions:
- createKeyValuePair: Allocates memory for a new key-value pair and initializes its values.
- createHashTable: Allocates memory for a new hash table and its array of pointers.
- insertWord: Inserts a word into the dictionary hash table, handling collisions with linked lists.
- isWordInDictionary: Checks if a word is in the dictionary hash table.
- freeHashTable: Frees the memory allocated for the hash table.
- Main Function (main):
- Creates a hash table to store the dictionary.
- Loads dictionary words into the hash table.
- Asks the user to input a word for spelling checking.
- Converts the input word to lowercase for case-insensitive checking.
- Checks if the input word is in the dictionary and prints whether the spelling is correct or incorrect.
- Frees the allocated memory.
Flowchart
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to implement a spell checker using a hash table that suggests corrections based on similar hash values.
- Write a C program to implement a case-insensitive spell checker that ignores punctuation by using a custom hash function.
- Write a C program to implement a spell checker that dynamically updates its hash table as new words are added to the dictionary.
- Write a C program to implement a multilingual spell checker that loads multiple dictionaries into a hash table with language selection.
Go to:
PREV : Generic Hash Table Challenges.
NEXT : C Programming Tree Exercises Home.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
