C Exercises: Check whether a given number is a perfect number or not
27. Perfect Number Check
Write a C program to check whether a given number is a 'Perfect' number or not.
A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors, excluding itself. For example, the number 6 is a perfect number because its divisors are 1, 2, and 3, and the sum of these divisors is 6.
Visual Presentation:

Sample Solution:
C Code:
/*
Perfect number is a positive number which sum of all positive divisors excluding that number is equal to that number.
For example, 6 is a perfect number since the divisors of 6 are 1, 2, and 3. Sum of its divisors is 1 + 2 + 3 = 6
*/
#include <stdio.h> // Include the standard input/output header file.
void main()
{
int n, i, sum; // Declare variables for user input, loop control, and sum.
int mn, mx; // Variables mn and mx are declared but not used. Consider removing them.
printf("Input the number : "); // Prompt the user for input.
scanf("%d", &n); // Read the value of 'n' from the user.
sum = 0; // Initialize the sum variable.
printf("The positive divisors : "); // Print a message to indicate positive divisors are being displayed.
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) // Loop to find and display positive divisors.
{
if (n % i == 0) // If 'i' is a divisor of 'n'.
{
sum = sum + i; // Add 'i' to the sum.
printf("%d ", i); // Print 'i' as a positive divisor.
}
}
printf("\nThe sum of the divisors is : %d", sum); // Print the sum of the divisors.
if (sum == n) // Check if the sum of divisors is equal to the original number.
printf("\nSo, the number is perfect."); // If true, print that the number is perfect.
else
printf("\nSo, the number is not perfect."); // If false, print that the number is not perfect.
printf("\n"); // Print a new line for better formatting.
}
Output:
Input the number: 28 The positive divisors: 1 2 4 7 14 The sum of the divisors is: 28 So, the number is perfect.
Input the number: 10 The positive divisors: 1 2 5 The sum of the divisors is: 8 So, the number is not perfect.
Explanation:
- Header inclusion:
- #include <stdio.h>: Includes the standard input/output header file for using functions like printf and scanf.
- Main function:
- int main(): The main function where the program execution begins.
- Variable Declaration:
- int n, i, sum;: Declares three integer variables:
- n for storing the user's input number.
- i for loop control.
- sum for storing the sum of the divisors.
- User input:
- printf("Input the number: ");: Prompts the user to input a number.
- scanf("%d", &n);: Reads the input number from the user and stores it in the variable n.
- Initial sum:
- sum = 0;: Initializes the sum variable to zero.
- Print Divisors Message:
- printf("The positive divisors: ");: Prints a message indicating the start of the list of positive divisors.
- Finding Divisors:
- for (i = 1; i < n; i++): A loop that runs from 1 to n-1 to find all positive divisors of n.
- if (n % i == 0): Checks if i is a divisor of n (i.e., if n modulo i is 0).
- sum = sum + i;: Adds i to the sum if i is a divisor.
- printf("%d ", i);: Prints the divisor i.
- Print Sum of Divisors:
- printf("\nThe sum of the divisors is: %d", sum);: Prints the total sum of the divisors.
- Check Perfect Number:
- if (sum == n): Checks if the sum of the divisors equals the original number n.
- printf("\nSo, the number is perfect.\n");: If true, prints that the number is perfect.
- else printf("\nSo, the number is not perfect.\n");: If false, prints that the number is not perfect.
- Return Statement:
- return 0;: Returns 0 to indicate successful execution of the program.
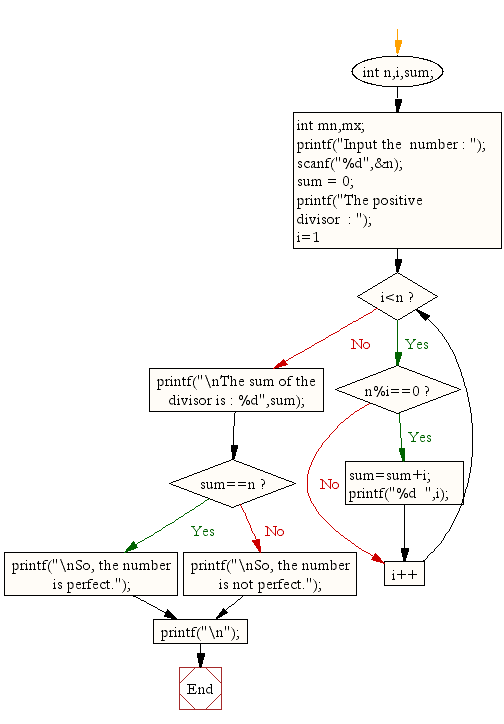
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to check if a number is perfect by summing its proper divisors using recursion.
- Write a C program to verify a perfect number and then list its proper divisors in descending order.
- Write a C program to check if a number is perfect without using loops, employing recursion only.
- Write a C program to check a range of numbers for perfection and count how many perfect numbers are found.
Go to:
PREV : Sum of Series 1 + 11 + 111 + ….
NEXT : Find Perfect Numbers in a Range.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
