C Program to Print numbers from 1 to 10 and 10 to 1 using Do-While Loop
1. Print Numbers Using Do-While Loop
Write a C program to print numbers from 1 to 10 and 10 to 1 using a do-while loop.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i = 1; // Initialize the loop control variable to 1
// Print numbers from 1 to 10
printf("Print numbers from 1 to 10:\n");
do {
printf("%d ", i); // Print the current value of i
i++; // Increment i for the next iteration
} while (i <= 10); // Continue the loop as long as i is less than or equal to 10
printf("\n"); // Move to the next line for better formatting
i = 10; // Reset i to 10 for the second part of the program
// Print numbers from 10 to 1
printf("\nPrint numbers from 10 to 1:\n");
do {
printf("%d ", i); // Print the current value of i
i--; // Decrement i for the next iteration
} while (i >= 1); // Continue the loop as long as i is greater than or equal to 1
return 0; // Indicate successful program execution
}
Sample Output:
Print numbers from 1 to 10: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Print numbers from 10 to 1: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Explanation:
Here is the break down of the above code step by step:
- #include <stdio.h>: This line includes the standard input-output library, which is necessary for using functions like "printf() and "scanf()".
- int main() {: This line marks the beginning of the "main()" function, which is the entry point of every C program.
- int i = 1;: This line declares an integer variable 'i' and initializes it to 1. This variable will be used as a loop control variable.
- // Print numbers from 1 to 10: This comment indicates the intention of the following code block.
- do {: Marks the beginning of a do-while loop. The code inside the curly braces will be executed at least once before checking the loop condition.
- printf("%d ", i);: Prints the current value of 'i' using the "printf()" function.
- i++;: Increments the value of 'i' by 1 for the next iteration.
- } while (i <= 10);: Specifies the loop condition. The loop will continue to execute as long as the value of i is less than or equal to 10.
- printf("\n");: Moves to the next line for better formatting.
- i = 10;: Resets the value of 'i' to 10 for the second part of the program.
- // Print numbers from 10 to 1: Comment indicating the intention of the following code block.
- do {: Starts another do-while loop.
- printf("%d ", i);: Prints the current value of 'i'.
- i--;: Decrements the value of 'i' by 1 for the next iteration.
- } while (i >= 1);: Specifies the loop condition for the second loop. It continues as long as i is greater than or equal to 1.
- return 0;: Indicates that the program executed successfully. The 0 here is typically used to indicate successful execution.
- }: Marks the end of the "main()" function.
In summary, this program uses two do-while loops to print numbers in ascending order (1 to 10) and then in descending order (10 to 1), separated by a newline for better output formatting. The loop control variable i is incremented in the first loop and decremented in the second loop. The program then returns 0, indicating successful execution.
Flowchart:
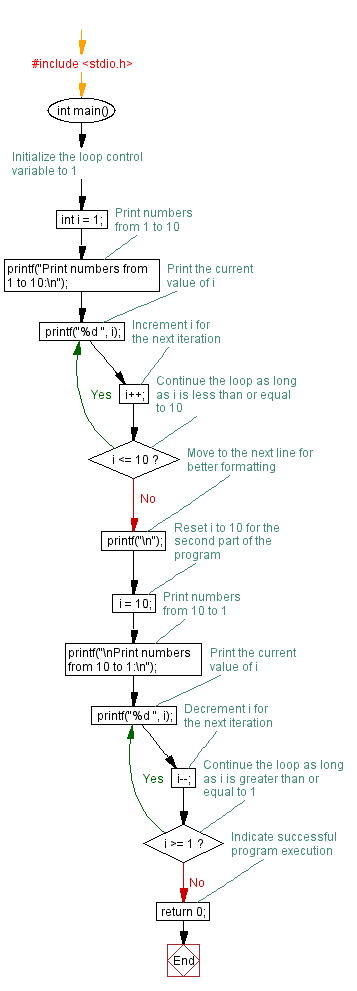
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to print numbers from 1 to 20 in ascending and then descending order using a do-while loop.
- Write a C program to print only prime numbers from 1 to 50 using a do-while loop.
- Write a C program to print numbers from 1 to 10 in reverse order without using the decrement operator.
- Write a C program to print numbers from 1 to 10 but skip every third number using a do-while loop.
Go to:
PREV : C Do-While Loop Exercises Home
NEXT : Sum of Positive Integers Until 0.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
